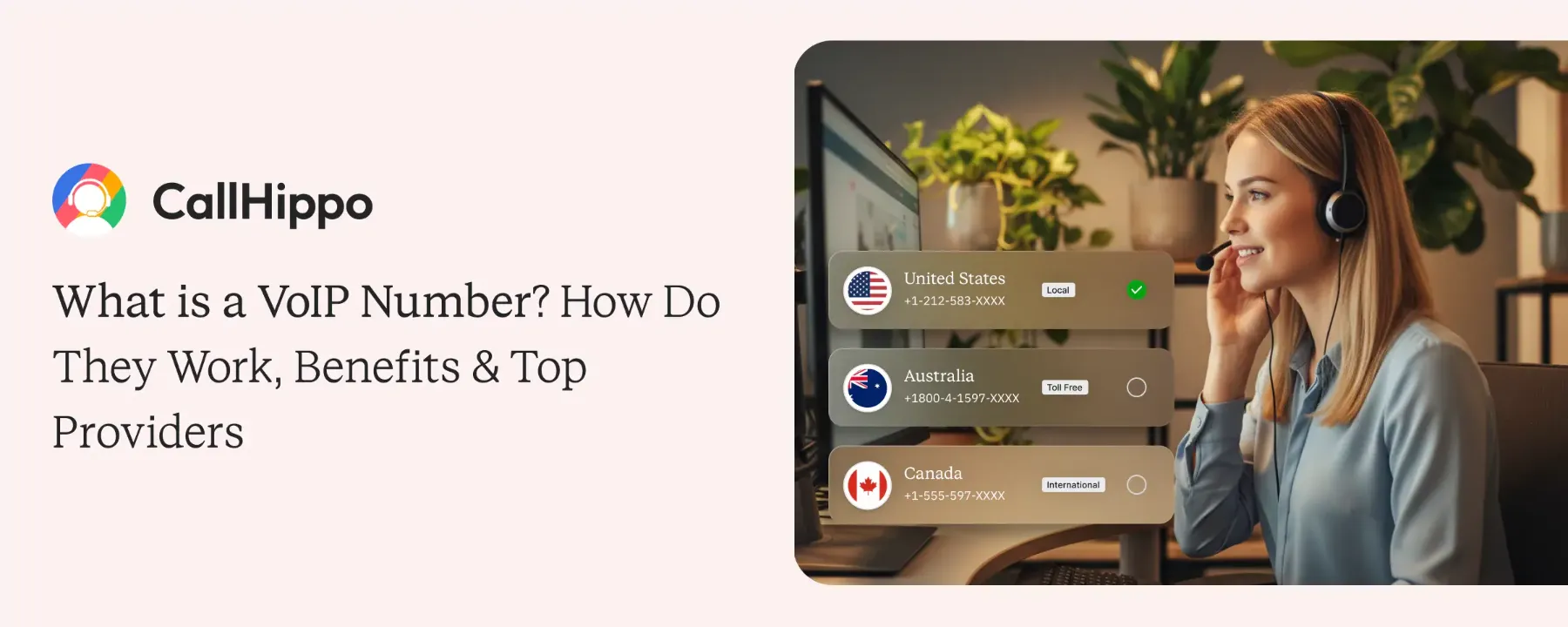
The VoIP Phone System Built for Teams That Sell and Support Globally
CallHippo is a VoIP phone system built for teams that sell and support across borders. You can make calls over the internet, ditch carrier rates, and go live in under 3 minutes with local numbers in 50+ countries.
- Make and receive calls from any device, anywhere in the world.
- Cut international call costs by up to 90% without carrier contracts or hardware.
- Add different country’s numbers instantly as your business grows.
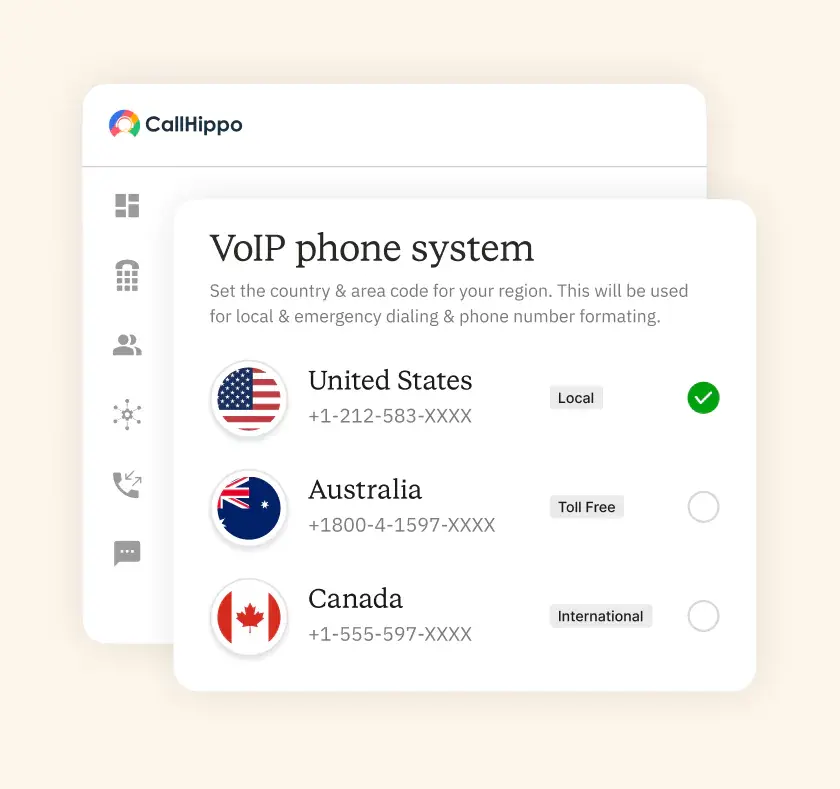
Switch to VoIP in 3 Steps [No IT Team Required]
On-premise PBX hardware, installation, phones, and software licenses add up to 70% of your expenses before your team makes a single call. CallHippo’s record setup time is 3 minutes. Here’s how it works.
Choose your plan, then select the countries and number types you need: local, toll-free, or mobile. Numbers in most of our 50+ supported countries go live within minutes of being selected. There's no provisioning queue, no carrier paperwork, and no wait for a technician. You can have a US number, a UK number, or a Singapore number active simultaneously.
Porting your existing numbers to CallHippo takes 7–14 business days. Critically, your old system keeps operating throughout the entire transfer. Not a single inbound call is lost mid-migration. New numbers in a new country? Those are instant. Either way, your team is never without a live line during the switch.
Send invite links by email. Your team opens CallHippo on iOS, Android, Windows, Mac, or any web browser, and they're live. No hardware to ship. No drivers to install. No IT request needed. A rep in Austin and a support agent in Manila share the same number, the same dashboard, and the same call quality from day one.
Everything You Get with CallHippo’s VoIP Phone System
Business leaders say the phone is one of their main communication tools. Here’s what changes when that tool is a cloud VoIP phone system built for how modern teams actually work.
Crystal-clear audio on redundant servers, backed by a 99.95% uptime SLA-less than 53 minutes of downtime per year. No drop, no degraded lines.
Local, toll-free, and mobile numbers that establish presence without offices. Calls from a local number are answered 4x more often than unknown or international caller IDs.
Voice, SMS, WhatsApp, email, Telegram, and Facebook Messenger: one shared inbox your whole team works from. Assign conversations and resolve customer queries together without teammates duplicating responses.
Multi-level IVR in 25+ languages routes callers without a receptionist. Customers actively prefer self-service options. A well-configured IVR serves that expectation immediately.
Every call is recorded, AI-transcribed, and stored in a searchable archive. Your recorded calls are the training data that gets you there.
Native integrations with Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho, Pipedrive, Freshdesk, and 50+ more. Teams using integrated VoIP-CRM systems report 30–50% more productive call time. Call log automatically without manual entry.
Call volume, wait times, agent performance, and custom reports are live. 83% of companies have lost customers due to communication failures they didn't see coming. These dashboards show the problem before the customer feels it.
iOS, Android, Windows, Mac, Chrome extension, web browser-the same number everywhere. 74% of employees already use a mobile app for work calls. CallHippo meets them on the device they're already holding.
What Are the Benefits of a VoIP Phone System?
A VoIP business phone system helps businesses communicate smarter. It brings better call quality, quick setup, useful integrations, and real savings. The right solution makes growth and customer communication much easier.
Calls automatically route to the right agent, team, or device, and if no one answers, voicemail captures it instantly.
Sign up, pick your numbers, and invite your team -you're live in under 3 minutes with no hardware or IT support needed.
Clear audio, smart call routing, and professional IVR greetings make every interaction feel polished. Customers reach the right person faster, wait less, and get resolved on the first call.
Every call is logged, recorded, and tied to a timeline your team can review anytime. Analytics show who called, when, how long, and how it ended, which helps managers coach agents.
Cut local and international call costs significantly with CallHippo. Help your business save more every month and maximize communication ROI.
Add users, numbers, and countries instantly as your business grows, no hardware limits, no IT tickets, no lead time required.
Pricing
- 1 Free Phone Number
Toll-free number not included.
- Free WhatsApp Business API
- Voicemail
- Click To Dial
- AI Global Connect
Identify phone number's timezone before a call
- SMS (Text messages) & MMS
- Everything in Basic + Telephony
-
Unlimited Minutes (Includes Both Landline & Mobile Calling)
Free minutes are shared by all account users. Calling on special and premium numbers are excluded.
- 100 SMS (Text Messages)
Standard A2P charges apply.
- Basic Report Analytics
- Everything in Starter +
-
Unlimited Minutes (Includes Both Landline & Mobile Calling)
Free minutes are shared by all account users. Calling on special and premium numbers are excluded.
- 500 SMS (Text Messages)
Standard A2P charges apply.
- Call Recordings
- AI Reports / Analytics
Smart reports that summarize user & call activity.
- Everything in Professional +
-
Unlimited Minutes (Includes Both Landline & Mobile Calling)
Free minutes are shared by all account users. Calling on special and premium numbers are excluded.
- 1000 SMS (Text Messages)
Standard A2P charges apply.
- Dedicated Account Manager
- Custom Integrations
- Single Sign On (SSO)
Securely log into multiple apps with one set of credentials.
CallHippo vs. 7 VoIP Phone Systems You’re Probably Comparing
Choosing the best VoIP phone service for your team depends on size, use case, and how fast you need to scale. Here’s an honest breakdown of how leading business VoIP service providers compare, including where competitors genuinely lead.
| Provider | Best For | Pricing | Standout Feature | Biggest Limitation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
CallHippo
|
Mid-market going global fast | $1/user/mo | Fastest setup, most affordable global coverage across 50+ countries, no hardware, no long-term contracts. Number porting with zero service interruption | Fewer enterprise-grade compliance features than Cisco or Avaya deployments |
| 2 |
RingCentral
|
Large enterprises wanting everything in one platform | $20/user/mo | Largest integration ecosystem in the category. Connects to nearly every business tool. Strongest for teams deeply embedded in Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace | Most integrations are locked to higher tiers; add-ons push the total cost well above the base pricing |
| 3 |
Nextiva
|
Customer-facing teams needing built-in CRM | $15/user/mo | Genuinely strong built-in CRM and customer journey tools. Solid choice if support and sales share a workflow. 99.999% uptime guarantee | Voice calling only included from the Core plan ($30/mo); fewer international countries than CallHippo |
| 4 |
Dialpad
|
AI-first teams prioritising live transcription | $15/user/mo | Real-time AI transcription during calls and live agent coaching — best in class for teams that coach from conversations | CRM integrations and 24/7 support locked to Pro plan ($25/mo); international calling capped at 1,500 min/mo |
| 5 |
Ooma
|
Very small businesses and home offices | $19.95/user/mo | Plug-in hardware setup with zero learning curve. Fastest path to a professional-sounding phone for a 1–5 person operation | Limited integrations and poor scalability beyond very small teams |
| 6 |
Vonage
|
Developers needing API-level customization | $13.99/user/mo | Best-in-class CPaaS APIs for building custom call flows, programmable voice, and SMS automation. Highly flexible if your team can write code | Requires technical resource to unlock full API value; many features are paid add-ons; 1-year contract required on annual plans |
| 7 |
Grasshopper
|
Solopreneurs and freelancers | $14/mo (flat) | Simple virtual number with greetings and voicemail. Charged per account, not per user. Works for solo operators wanting a professional presence | No integrations on any plan; not built for teams; collapses quickly beyond 1–2 users |
| 8 |
CloudTalk
|
Support-heavy teams with high inbound volumes | $25/user/mo | Advanced inbound queue management, callback scheduling, and strong helpdesk integration. Built specifically for formal support operations | Fewer outbound sales tools; less suited to globally distributed SMBs needing rapid international expansion |
How Different Teams Use VoIP(It’s Not Just for Call Centers)
Each team type has a different bottleneck. Here’s the specific workflow transformation when that bottleneck is removed.
Sales Teams: Dial More, Close More
Most people don’t answer phone calls from unknown numbers, which means most cold outreach never gets heard. CallHippo’s local presence dialing shows a local caller ID in the prospect’s area, which studies show increases answer rates by 4x. Power dialer eliminates the dead time between calls; when one ends, the next begins without the rep touching a keyboard.
Every call auto-logs to your CRM with duration and outcome, so reps aren’t doing 20 minutes of post-call data entry. Managers can pull recordings to coach on exactly the moment that closes or loses a deal.
Customer Support: Resolve Faster, Scale Smarter
Customers expect a business to be reachable around the clock in some form. CallHippo’s IVR routes callers by issue type before they ever reach an agent, cutting handle time without cutting quality. Omnichannel inbox means the customer who opens a WhatsApp message at 9 am and calls at 11 am is treated as one continuous conversation, not two separate tickets.
Follow-the-sun routing sends calls to whichever regional team is online, so your customers in Singapore don’t wait for your London team to clock in. Ticket systems like Freshdesk sync automatically. The recording is already attached when the case opens.
Remote & Hybrid Teams: One System, Any Location
Hybrid roles have doubled since the COVID-19 pandemic. The phone systems most of these teams inherited weren’t designed for any of this. A shared CallHippo team number means customers always reach someone, not a personal mobile that nobody else can cover when an agent is out.
Browser calling means a new hire is live on their first day without IT touching their machine. A team spread across London, Nairobi, and Manila gets the same features, the same call quality, and the same dashboard. Location stops being a constraint the moment the system is cloud-native.
Enterprise Features Without Enterprise Costs
New businesses that choose VoIP from the start can cut their initial communication costs compared to building on PSTN infrastructure. The SMB segment is the fastest-growing in the global VoIP market because five-person startups now have access to the same multi-level IVR, international numbers, AI transcription, and CRM sync that enterprises once paid six figures for.
Start at $1/user, scale as you grow, cancel anytime. No contracts. No hardware procurement. No PBX to maintain. The money saved goes back into growing the business, not into keeping old infrastructure alive.
What Makes a VoIP Phone System Better Than What You Have Now?
The wholesale voice carrier market now runs on VoIP. In the US, the copper lines underpinning Avaya, Cisco on-prem, and Mitel systems have been declining at 17.8% every year since 2021, and that rate is accelerating.
Meanwhile, the teams your competitors are building right now are starting on cloud systems by default. Legacy PBX is a cost you’re carrying while everyone else moves faster.
| Capability | Traditional PBX | VoIP Phone System (CallHippo) |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Time | Weeks to months-hardware procurement, on-site cabling, IT configuration, carrier provisioning | Minutes from signup to first call. Numbers are active instantly. Team onboarded via invite link |
| Upfront Cost | $5,000–$50,000+ in PBX hardware, handsets, cabling, and installation fees. Ongoing maintenance contracts on top | $0 hardware. Pay per user, per month. No capital expenditure required. Cancel anytime |
| International Calls | High per-minute carrier rates. International presence means physical offices | Up to 90% lower international call costs. Local numbers in 50+ countries-no offices required |
| Remote Access | Typically requires VPN and IT support. Desk phone tied to a physical location | Full functionality on any device, any location. 74% of employees already use mobile for work calls |
| Scalability | Adding lines requires hardware capacity checks, IT tickets, and sometimes a full system upgrade | Add users in 30 seconds. Remove them the same way. No hardware ceiling |
| CRM Integration | Little to no without expensive custom middleware. Data lives in silos | Native integrations with 50+ CRMs. Calls auto-log. 30–50% more productive call time reported after switching |
| Analytics | Basic call logs, often requiring manual export and reporting | Real-time dashboards, agent performance metrics, custom reports- updated live |
| Maintenance | Requires dedicated IT. Hardware failures cause outages. Physical parts degrade over time | Cloud-managed. Updates automatic and invisible. Redundant failover means no single point of failure |
Get Started with a VoIP Phone Number You Can Trust
Discover how easy it is to set up your VoIP phone number with CallHippo and see how our clients improved communication and customer satisfaction.


“Thanks to the CallHippo team, we were able to resolve a tough issue with flagged phone numbers. As an EdTech startup, outbound calls are crucial for us. CallHippo's solution not only improved our attestation score but also boosted our answer rates and overall customer experience.”
Frequently Asked Questions
-
A minimum of 100 Kbps per concurrent call is sufficient for good voice quality, and that's a conservative estimate, including network overhead. VoIP also uses silence suppression during pauses, which reduces actual bandwidth consumption. Most standard business broadband connections handle a full team without any QoS configuration needed.
-
Yes. Number porting transfers your existing business number to CallHippo in 7–14 business days for standard local numbers; complex or multi-number ports may take longer. Your current system stays live throughout the transfer, so no calls are missed mid-migration. You can also port numbers away from PSTN and ISDN lines before those networks reach their end-of-life.
-
CallHippo's 99.95% uptime SLA equals less than 53 minutes of downtime annually, and unlike physical PBX hardware, failures in one cloud node are automatically rerouted, invisible to your team. Businesses report an improved security and reliability posture after migrating from on-premise to cloud-based communications.
-
No. CallHippo runs on any smartphone, laptop, or web browser your team already uses. If you prefer a physical desk phone, VoIP-compatible IP phones work too, but they're optional. The practical result: no hardware procurement, no shipping lead time, no IT setup. A new hire can be making calls from their laptop before their first meeting ends.
-
CallHippo encrypts all calls using TLS and SRTP, with GDPR-compliant data handling. Cloud migration consistently improves security posture. Migrated businesses confirm this. Enterprise plans add SSO, audit logging, and advanced access controls for teams with stricter compliance requirements, such as HIPAA or SOC 2 environments.
-
Yes, and this integration is one of the highest-impact changes that comes with switching. Teams using combined VoIP and CRM systems report more productive call time. CallHippo has native integrations with Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho, Pipedrive, Freshdesk, and 50+ others. Every call logs automatically- no manual entry, no data lag.
-
VoIP systems include call forwarding rules that automatically route incoming calls to a mobile number or another line if your internet connection drops. You configure the failover rules in advance from your dashboard so customers never hit a dead end. This kind of failover setup is standard across VoIP platforms. Check CallHippo's specific plan features for what's included at each tier.
-
Significantly. VoIP cuts local and international call costs. Businesses migrating off legacy phone systems save on mobile and long-distance calling. Subscription-based VoIP also reduces installation costs compared to PSTN buildout-no cabling, no hardware, no technician visit.
-
Yes. CallHippo provides local, toll-free, and mobile numbers in 50+ countries, active within minutes of selecting them. You can run a US number, a UK number, and a Singapore number simultaneously- all from one dashboard, all answered by the same team. Calls from those local numbers are answered 4x more often than calls from international or unknown caller IDs.
-
Yes, no credit card required. HD calling, CRM integration, the omnichannel inbox, and analytics are all available during the trial, not a stripped-down preview. Setup takes under 3 minutes. If you're comparing CallHippo against other VoIP providers, the trial is the fastest way to evaluate real call quality under your actual network conditions.