Has it ever happened to you that you were trying to have a conversation on a call and the voice on the other end distorted due to a poor internet connection? You must have found yourself asking, “Can you hear me?”
Frustrating, right?
This issue is often caused by internet jitter. So, what is internet jitter?
Internet or network jitter is the fluctuation in the timing of packets traveling across the network that can affect communications like VoIP or video calls.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through the meaning of jitter, its causes, and effective ways to reduce it.
Busy? Here's Quick Overview
Network jitter refers to the variation in the delay of incoming data packets as they travel across a network. Ideally, packets should arrive at consistent intervals, but jitter occurs when there is fluctuation in the timing of these packet arrivals. It can result in delays or disruptions in real-time communication services like VoIP, video streaming, and online gaming.
- Impact Areas:
- VoIP Calls: Jitter causes audio quality distortion, lost words, and dropped calls, with conversation sound more garbled and maddening.
- Streaming: Jitter causes buffering, pixeled video, and lost audio, causing interruptions in viewing, particularly live streams or high-definition video.
- Online Gaming: Jitter causes lag and delayed movement in the game, which slows down players’ reactions and puts gamers at a disadvantage.
- Causes behind Jitter: There are several reasons behind jitter, including network overload, device saturation, ISP, and a misconfigured router. Also, wireless network connection experiences a lot of jittering due to interference and proximity to the router.
- Fixing Jitter: In order to minimize jitter, you can tweak network configurations, utilize wired networks, refresh the router, and apply Quality of Service (QoS) to give preference to real-time traffic. For your business, the adoption of AI-based VoIP solutions such as CallHippo will minimize jitter by optimizing call quality with ease of communication.
What is Network Jitter?
Network jitter is the inconsistency in the time it takes data packets to travel across a network. It can cause delays, lag, or choppy audio/video in real-time communications like VoIP or video calls.
Imagine you send a series of packages through the postal service, and they should ideally reach your friend’s house at the same time. However, sometimes one package might arrive earlier, while the next one arrives later.
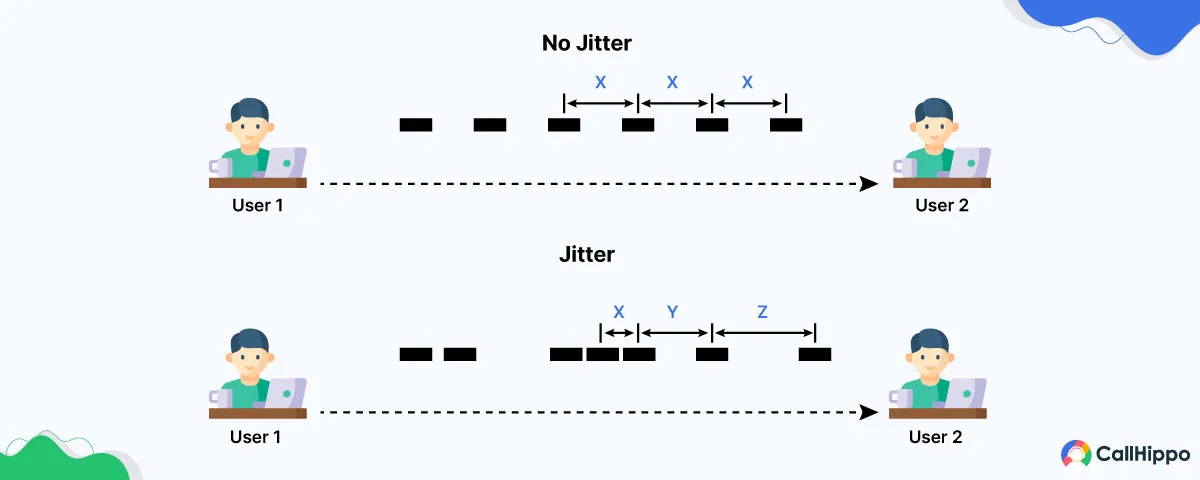
Jitter is like that – it happens when data (like audio quality or video) is sent over the internet in small packets. Instead of these packets arriving at regular times, some arrive too early, and others too late. This causes delays or interruptions, especially when you’re on a call, streaming a video, or playing a game online.
This variability can have a negative impact on the performance of internet-based services, leading to problems such as lag or degraded audio and video quality.
How Latency Differs from Jitter?
Latency refers to the delay in the time it takes for data packets to travel from one point to another. Think of it as the time it takes for a letter to go from one person to another. If the delay is high, you’ll notice a lag. According to Cisco’s guidelines, for VoIP applications, the maximum acceptable one-way latency is 150 milliseconds (ms).
Jitter is the inconsistency in the timing of data packets arriving. If some letters arrive on time, but others arrive too early or too late, that’s jitter. It causes disruptions like audio or video cutting in and out during internet phone calls or streaming. Cisco’s guidelines suggest that for VoIP applications, the acceptable level jitter is under 30 ms.
Key Difference:
- Latency is how long it takes for multiple data packets to travel.
- Jitter is how inconsistent the travel time is, causing interruptions.
The Impact of Jitter on VoIP and Streaming
As per the internet provider’s protocol, jitter has a strong effect on any service that is dependent on the flow of incoming data packets. The most evident and harmful effects appear in real-time communication services such as VoIP, streaming, and online games.
| Service | Jitter Impact | Effect on User Experience |
|---|---|---|
| VoIP Calls |
| Communication becomes unclear, leading to frustration. |
| Streaming Video |
| Interruption in video playback, loss of quality. |
| Online Gaming |
| Poor gaming experience, competitive disadvantage. |
| Business Communication |
| Delayed decision-making, decreased productivity. |
| Customer Service |
| Decreased customer satisfaction, frustration during support. |
1. In VoIP jitter, conversations become unintelligible. Mostly, words will be lost and sentences might sound muddled, which can disrupt the continuity of communication. This is especially a problem in business environments, where clear, consistent communication is paramount.
2. For both video and audio streaming, jitter can cause pixelated video, dropped audio quality, or buffering. These types of discontinuities can be frustrating to users, especially in real-time streaming events, where smooth, continuous playback is the bare minimum.
3. In games, jitter can ruin the overall experience. According to one survey, jitter results in lag, where the player’s inputs are delayed. These interruptions make the game feel unresponsive in competitive environments.
4. For your business, jitter can become a nuisance. Jitter is correlated with customer service and the productivity of your staff. Unpleasant distortion in the client communication can hamper customer satisfaction, damage the reputation of your company, and lead to customer churn. For your company staff, broken meetings or conference calls can delay the overall decision-making processes.
Jitter disrupts call quality and customer experience. CallHippo reduces jitter for clear, reliable conversations every time.
What Causes Jitter on a Network?
There are various causes of jitter, which can be either short-term or long-term. You can troubleshoot and avoid jitter issues by referring to the causes.
1. Network Congestion
If different devices (like phones, laptops, TVs, etc.) are accessing the same network simultaneously, then the network connection can become crowded. It may lead to a backlog and result in delays of packets. Also, an inadequate bandwidth can lead to buffering and jitter.
Example: You might experience jitter while streaming a movie if another one is being downloaded at the same time.
2. Hardware Constraints
Ineffective hardware is the root cause of delayed packet arrival. Poorly manufactured routers, modems, or old network gear might be insufficient to deal with a high volume of data packets and lead to jitter.
Example: If you're working with an outdated router, even simple browsing may cause some inconsistency in your network traffic and speed.
3. Wireless Network Connection
Wi-Fi links are more prone to jitter compared to wired links due to interference with the signal, network overload, and range limitations.
Example: A router positioned far from a device may be responsible for weak Wi-Fi signals, resulting in packet loss and jitter.
4. ISP Issues
Issues in the infrastructure of an Internet Service Provider, i.e., routing inefficiency, can create jitter. This is usually experienced when ISPs become subject to too much traffic or network misconfigurations.
Example: At peak hours, your internet speed may experience random variations because of your ISP's network saturation.
5. Router or Server Misconfigurations
Misconfigurations in the devices can cause loss of packet flow and create jitter. This is bound to happen in poorly administered business networks or poorly configured home networks.
Example: If your router firmware is old or not properly configured, it may not process traffic well. Thus, multiple data packets get delayed while letting less significant packets travel faster, and jitter occurs.
6. Physical Barriers in the Network
Barriers such as solid walls or other electronic devices causing interference can result in unstable network signals. It leads to jitter in wireless networks.
Example: If your Wi-Fi signal has to travel through numerous walls, it will arrive at irregular intervals and cause jitter.
Switch to CallHippo
- Smooth Conversations
- Stable Connection
- Enhance Customer Experience
How to Measure Internet Jitter?
Measuring jitter assists you in determining the fluctuations in data packet timing that might impact the quality of your network services. Here, we have come up with a few techniques for instantaneous jitter measurement:
| Method | What It Measures | How to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Ping Test | Measures packet round-trip time. | Run ping[server]-t in Command Prompt or Terminal. |
| Network Monitoring | Analyzes jitter in real-time traffic. | Use tools like Wireshark or SolarWinds for continuous monitoring. |
| Speed Test Websites | Measures jitter along with speed. | Visit websites like Speedtest.net and run the test. |
| Traceroute | Traces packet routes and measures delays. | Type tracert[server] in Command Prompt or Terminal. |
1. Ping Test
A ping jitter test is one of the easiest ways to measure network jitter. It sends packets to a destination and measures how long it takes for each packet to come back. Ideally, each packet should come back at the same time, but jitter buffer happens when there is a fluctuation in the round-trip time of the packets.
How to do it:
- Open the Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (Mac/Linux).
- Type the command ping [server address] -t and hit enter (e.g., ping google.com -t).
- This will send continuous ping requests to the server. Observe the times shown in milliseconds (ms).
- If the ping times vary significantly, you’ll know jitter is present.
Interpreting the findings: Widely fluctuating ping times mean that jitter is impacting the connection. For example, ping times that consistently range by over 20 ms may lead to frequent issues with real-time services.
- Always perform ping test on a reliable and stable server such as 8.8.8.8 (Google DNS) or google.com. As long as possible, avoid ping test of random websites as they can be unsecure.
2. Network Monitoring Tools
If you are looking for a more professional solution, then try network monitoring software. These tools can take more accurate readings of jitter and give substantial insight into how well your network performs.
Here’s a list of the widely used network monitoring tools:
- Wireshark
- Nagios
- SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor
- PRTG Network Monitor
- Zabbix
- ManageEngine OpManager
- NetFlow Analyzer
- Cacti
- Icing
- Splunk
How to use these tools:
- Install and configure the tool to monitor the specific network or device you’re concerned about.
- Begin your analysis and look for graphs or tables that track jitter over time. These tools may also indicate where jitter is occurring along your network path (e.g., at certain routers or network segments).
3. Speed Test Websites
Numerous speed test websites also check jitter along with your internet speed. Sites such as Speedtest.net, Fast.com, and TestMy.net offer an easy method to test jitter and upload speeds.
How to use them:
- Visit one of these sites and run a speed test.
- The test results will usually have a measurement for jitter in milliseconds (ms), which shows the amount of variation in the timing of the packets.
- Measured in milliseconds ms, jitter is usually acceptable if it is less than 30 ms. Anything above can cause noticeable interruptions to real-time applications such as VoIP traffic and video calls.
Interpreting results: If the jitter is constantly high, it indicates that your internet connection is probably unstable. So, you might have low-quality calls or buffering when streaming.
4. Traceroute
Traceroute is a command-line utility to assist you in determining the exact path the packets travel over any network, including the intermediate routers (or hops) they traverse. This utility not only displays average latency but also displays jitter along the network path.
How to do it:
- Open the Terminal (Mac/Linux) or Command Prompt (Windows).
- Type tracert [server address] (Windows) or traceroute [server address] (Mac/Linux) and hit enter (e.g., tracert google.com).
- This will display the path and the time taken for each hop.
Interpreting the results: If you see one or more hops with variable response times (large spikes in ms between hops), this is strong evidence that jitter exists. The problem might be limited to a specific router or network segment.
How to Reduce Jitter on Wi-Fi and Wired Networks?
Minimizing jitter is extremely important in order to give uninterrupted and smooth communication. Here are some of the ways that you can leverage to minimize jitter and improve your network performance:
(Make the image of bullets below, with alt text: Strategies to Reduce Jitter on Wi-FI and Wired Networks)
1. Use Quality of Service (QoS)
QOS permits a certain type of internet traffic to be given priority over others. Having your router configured to provide real-time traffic priority (e.g., VoIP telephone calls, video streaming, or internet gaming) ensures that such packets are delivered with minimal delay.
For instance, voice packets for a VoIP call will be assigned a higher priority task that will reduce delays and interruptions from less important data traffic, such as web browsing or downloading.
2. Reduce Network Congestion
Excessive use of streams, either for streaming videos or for downloading large files, may lead to congestion, which ultimately creates jitter. By limiting unnecessary bandwidth usage at peak hours (such as work calls or meetings), you can minimize jitter and provide a better service experience for real-time applications. Also,
- Data packet prioritization allows more efficient use of network resources and minimizes network congestion.
3. Upgrade Your Router
Undeniably, the old and outdated routers can not handle high-bandwidth applications, and therefore, internet jitter problems may happen. Replacing the old router with a new router with better traffic handling capabilities can be a great jitter reducer, especially in networks where multiple devices are accessed simultaneously.
4. Switch to a Wired Connection
Ethernet connections are less prone to interference and are more stable in comparison to Wi-Fi. Always connect your router through an Ethernet cable for VoIP calls, video conferencing, or gaming for easy transmission of data lines and minimal jitter.
5. Optimize Router Placement
The physical placement of your router will influence the reliability and quality of your Wi-Fi signal. Make sure you are placing your router in the middle of your room, away from walls and electronic interference sources. This will surely increase signal strength and result in zero jitter due to strong router connectivity.
Wrapping Up
Understanding what network jitter is and its impact can help you identify and address recurring jitter problems.
When you take responsible actions like using a wired connection, optimizing network equipment, and contacting ISPs, you can improve the quality of your internet-based services and curb jitter. Reducing jitter ultimately enhances productivity, ensures smooth communication, and provides a better entertainment experience for users.
FAQs
1. Is Jitter Worse Than Latency for VoIP Calls?
Yes, jitter is worse than latency for VoIP calls. Jitter causes choppy audio and dropped words and makes communication unclear, while latency only introduces slight delays.
2. Can Changing My Router Fix Internet Jitter?
Yes, upgrading your router can fix jitter. Modern routers with QoS features prioritize real-time traffic, reducing jitter caused by congestion or outdated equipment.
3. How Do I Know if Jitter is Affecting My Network?
Signs of jitter include poor VoIP call quality, video buffering, or delayed actions in gaming. You can use tools like ping tests or network monitors to check for fluctuations in packet timing.

Subscribe to our newsletter & never miss our latest news and promotions.









