Voice-over Internet Protocol (VoIP) codecs serve for a lot more than just recording and decompression.
They are advanced algorithms that influence the quality, efficiency, and overall experience of your business’s VoIP communications.
Understanding VoIP codecs and their impact on call sound quality is crucial for both users and service providers.
Read along as we discuss the key components of Codec VoIP and how to choose the right one to ensure optimal call quality.
When choosing a VoIP codec, prioritize your network's bandwidth capacity and desired call quality. Narrowband codecs like G.729 are efficient for limited bandwidth, while wideband codecs like G.722 offer superior audio clarity for high-definition calls.
What are VoIP Codecs?
VoIP codecs are algorithms used to encode and decode voice data for transmission over the internet. The term “codec” stands for “coder-decoder” or “compressor-decompressor.” In essence, codecs compress audio signals into data packets for transmission and then decompress them back into audio signals at the receiving end.
This process enables efficient and high-quality voice communication over IP networks. Since the call is made over the internet, the audio codec determines call quality and latency.
Key Components of VoIP Codecs
While the total process of recording, converting, sending, and playing back voice involves numerous components in a VoIP system, the voice codec itself has several important characteristics to consider:
1. Sub-Band Coding
Sub-band coding is a method where the audio signal is divided into multiple frequency bands. Each band is then encoded separately, which allows for better compression and reduced bandwidth usage. This technique is effective in preserving voice quality while minimizing the data size.
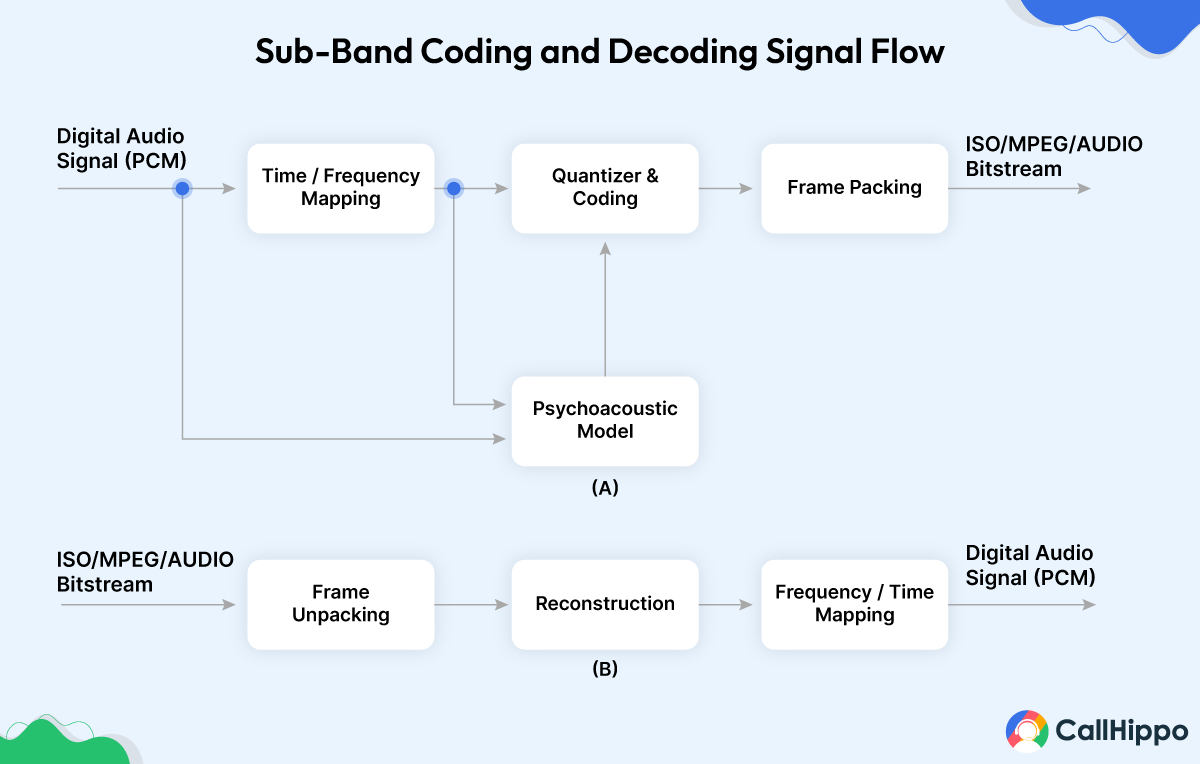
Sub-band coding is used in the G.722 codec, which uses sub-band adaptive differential pulse code modulation (SB-ADPCM) within a bit rate of 64 kbit/s. The SB-ADPCM approach divides the frequency range into two sub-bands (upper and lower), and the signals in each sub-band are encoded using ADPCM.
2. Linear Predictive Coding (LPC)
Linear Predictive Coding is a technique used to model the vocal tract and predict future audio samples based on past samples. LPC reduces the amount of data needed to represent the voice signal by eliminating redundancies.
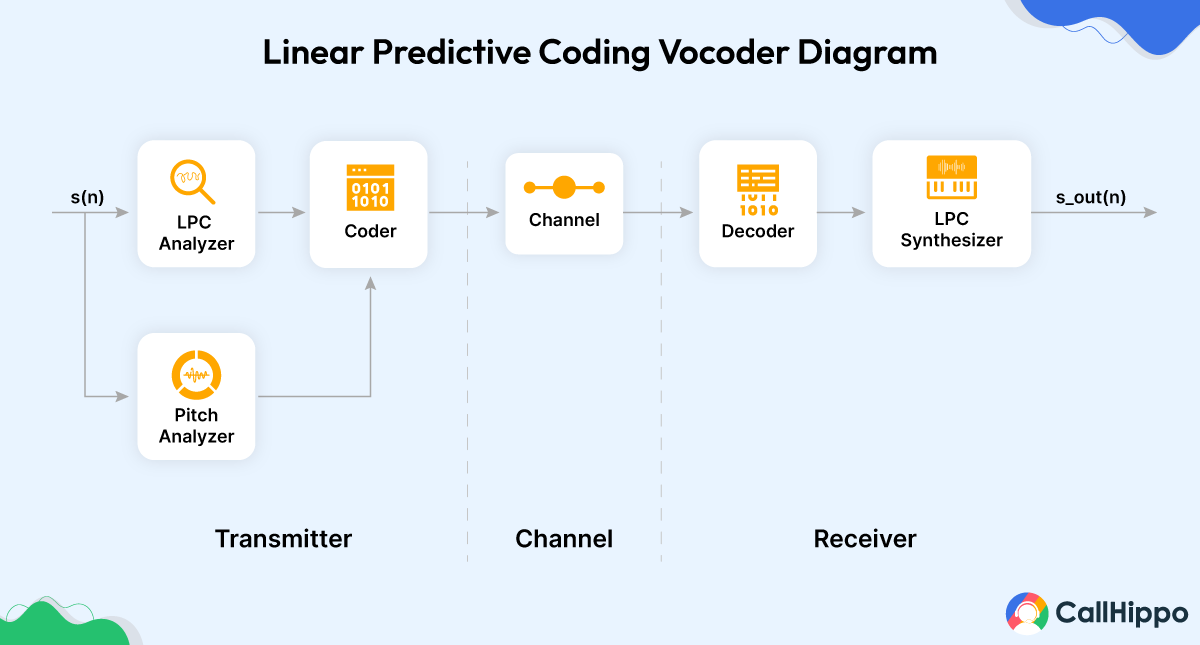
LPC is the most widely used method in speech coding and speech synthesis. It is a powerful speech analysis technique and a useful method for encoding good-quality speech at a low bit rate.
3. Vector Quantization (VQ)
Vector Quantization is a method of compressing voice data by converting it into a series of vectors. These vectors are then mapped to a finite set of codebook vectors.
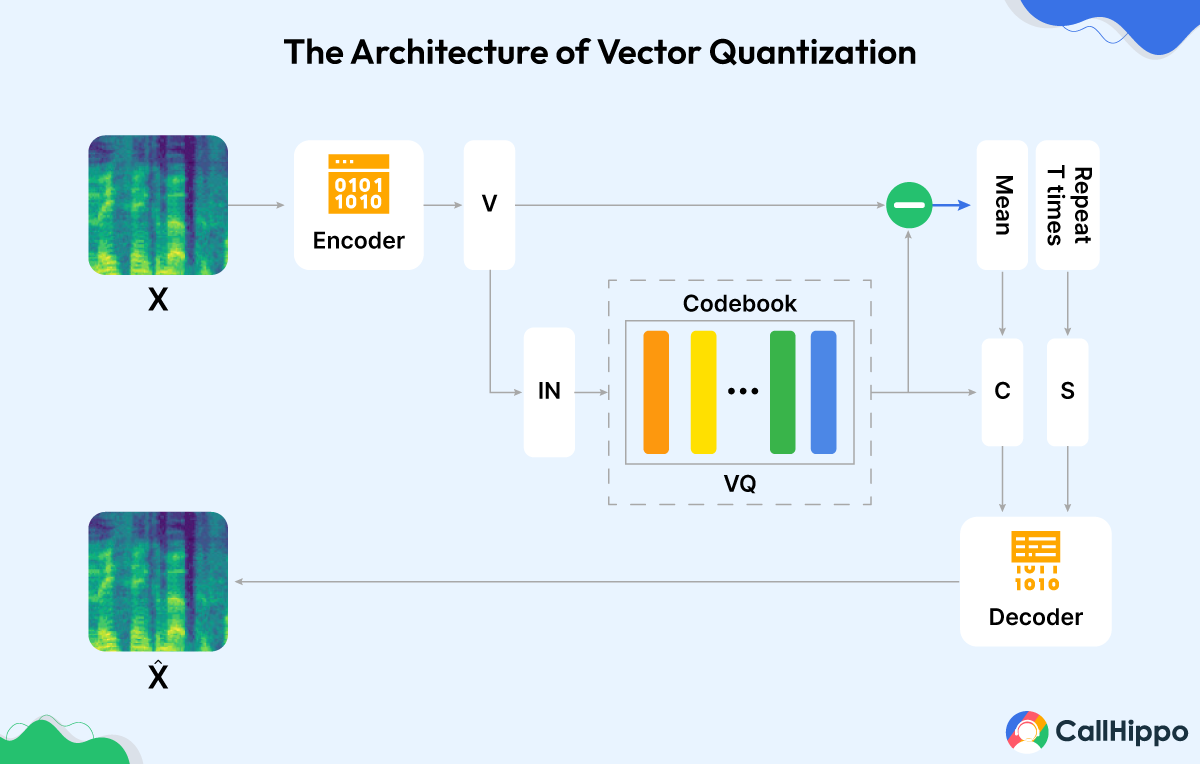
VQ is effective in reducing data rates while maintaining a good level of speech quality. It is commonly used in conjunction with other coding techniques for enhanced compression.
How Do VoIP Codecs Work?
VoIP audio codecs work by digitizing analog voice signals, compressing the data, and transmitting it over IP networks. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how this process works: Image:
1. Analog to Digital Conversion
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) converts analog voice signals into a digital signal. This procedure takes regular speech signal samples and digitally saves the voice waveform amplitudes at each sample.
2. Encoding
The digital signal is compressed using a codec. This involves eliminating redundancies and unnecessary information to reduce the size of the data. A few well-known codecs are G.711, G.729, Speex, and OPUS.
3. Packetization
The compressed data is divided into packets, which are then transmitted over the internet. The IP network can then be used to send these voice packets.
4. Decoding
The packets travel across the network to the recipient’s device. The recipient’s device uses a codec to decompress the data back into a digital voice signal.
5. Digital to Analog Conversion
Finally, the digital signal is converted back into an analog signal using a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) and played through the recipient’s speaker.
What are the VoIP Codec Types?
The common VoIP codecs can be classified into various types based on their bandwidth usage and voice quality. The main types include:
1. Narrowband Codecs
Narrowband codecs operate within a frequency range of 300-3400 Hz, which is sufficient for standard voice communication. These codecs are designed to use minimal bandwidth, making them ideal for environments where network resources are constrained.
Despite the limited frequency range, narrowband codecs can provide clear and intelligible voice quality suitable for most telephony applications. Here are some commonly used narrowband codecs:
| G.711 | |
| Description | G.711 is a standard narrowband codec widely used in traditional telephony and VoIP systems. |
| Bitrate | It operates at 64 kbps. |
| Quality | G.711 offers high voice quality, equivalent to that of the public switched telephone network (PSTN). |
| Pros | Excellent voice quality with minimal latency |
| Cons | Higher bandwidth consumption compared to other narrowband codecs. |
| G.729 | |
| Description | G.729 is a popular narrowband codec designed for low-bandwidth usage while maintaining good voice quality. |
| Bitrate | It operates at 8 kbps. |
| Quality | Provides good voice quality with efficient compression. |
| Pros | Low bandwidth usage, suitable for congested networks. |
| Cons | Requires licensing fees, slightly lower voice quality compared to G.711. |
| G.726 | |
| Description | G.726 is an adaptive differential pulse code modulation (ADPCM) codec used for compressing voice data. |
| Bitrate | It operates at multiple bitrates, including 16, 24, 32, and 40 kbps. |
| Quality | Offers a balance between bandwidth usage and voice quality, with the 32 kbps mode being the most common. |
| Pros | Flexibility in bitrate selection based on network conditions. |
| Cons | Voice quality is generally lower than G.711, especially at lower bitrates. |
Narrowband codecs like these are essential for optimizing network efficiency while maintaining adequate voice quality. By selecting the appropriate codec based on your specific network conditions and communication needs, you can ensure a reliable and effective VoIP network.
2. Wideband Codecs
Wideband codecs, also known as HD codecs, operate over a broader frequency range of 50-7000 Hz or even higher. This extended range allows them to capture more of the details in human speech, resulting in clearer and more natural-sounding voice communication.
Wideband codecs are increasingly used in modern VoIP devices to enhance call quality. Here are some commonly used wideband codecs:
| G.722 | |
| Description | G.722 is a widely adopted wideband codec in VoIP and high-definition voice applications. |
| Bitrate | Operates at 48, 56, and 64 kbps. |
| Quality | Provides significantly better audio quality compared to narrowband codecs, capturing more speech details. |
| Pros | High voice quality with relatively low latency, standardized and widely supported. |
| Cons | Higher bandwidth usage compared to narrowband codecs. |
| Opus | |
| Description | Opus is a versatile and highly efficient codec designed for both narrow-band and wide-band applications, including voice and music streaming. |
| Bitrate | Operates over a wide range from 6 kbps to 510 kbps. |
| Quality | Exceptional audio quality across all bitrates, adaptable to network conditions |
| Pros | Open-source and royalty-free, highly flexible, excellent audio quality. |
| Cons | Higher computational requirements, though modern devices handle this efficiently. |
| AMR-WB (Adaptive Multi-Rate Wideband) | |
| Description | AMR-WB is a wideband codec specifically optimized for cellular networks and widely used in mobile communications. |
| Bitrate | It operates at rates ranging from 6.6 to 23.85 kbps. |
| Quality | Provides high quality audio communication in variable network conditions. |
| Pros | Optimized for mobile networks, it has good audio quality at lower bitrates. |
| Cons | Licensing costs, are higher complexity compared to some other codecs. |
Implementing wideband codecs in your VoIP infrastructure can lead to substantial improvements in communication quality, making them a valuable choice for businesses and individual users alike.
& start calling
- Buy Numbers
- Add Users
- Start Calling

How to Choose the Right Codec?
Choosing the best VoIP codec depends on several factors, including:
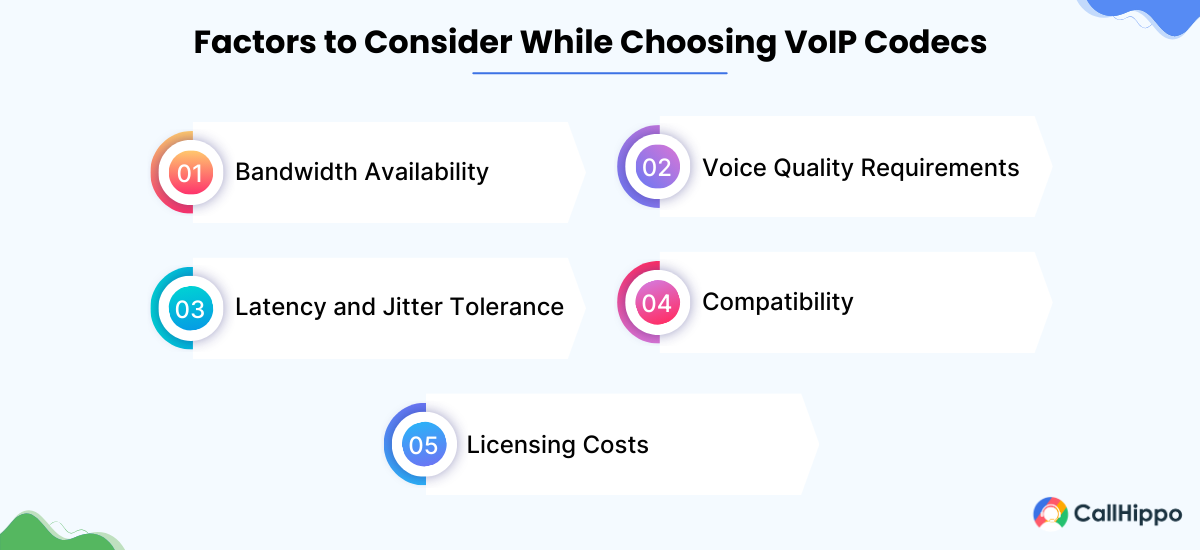
1. Bandwidth Availability
Assess your network’s bandwidth capacity. If bandwidth is limited, narrowband codecs like G.729 might be more suitable.
2. Voice Quality Requirements
Determine the level of voice quality needed. For high-definition audio data, wideband codecs like G.722 or Opus are ideal.
3. Latency and Jitter Tolerance
Consider the network’s latency and jitter characteristics. Some codecs are more resilient to these issues than others.
4. Compatibility
Ensure the codec is compatible with your VoIP hardware and software.
5. Licensing Costs
Some codecs, like G.729, require licensing fees, while others, like Opus, are open-source and free to use.
Conclusion
VoIP codecs are important for improving the efficacy and quality of voice communication through IP networks. You can improve your VoIP call experience by making well-informed judgments and being aware of the many kinds of codecs and their key components.
The correct codec must be chosen in order to achieve the greatest possible performance in VoIP systems; bandwidth efficiency or the highest possible audio quality should be the main priorities. The more your VoIP codec compresses audio data, the lower the audio quality.
FAQs
1. How do codecs improve call quality?
Codecs improve call quality by efficiently compressing and decompressing voice data, reducing bandwidth usage, and maintaining audio fidelity even at a slow internet connection. Advanced codecs, like wideband codecs, provide higher audio resolution, resulting in clearer and more natural-sounding voice calls.
2. How do devices negotiate which codec to use during a VoIP call?
During a VoIP call setup, devices exchange information about supported codecs through a process known as codec negotiation or codec selection. This involves signaling protocols like SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) to agree on a common codec that both parties support, ensuring compatibility and optimal call quality.
3. How to fix issues with codecs in VoIP systems?
To fix issues with codecs in VoIP systems, you need to check network quality and update software regularly. Apart from this, verify that codecs are properly configured. Additionally, you can implement Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize voice traffic over other types of data. However, you can contact your VoIP service provider for assistance if issues persist.

Subscribe to our newsletter & never miss our latest news and promotions.









