Communication is essential in this technology-driven world, where businesses and individuals alike seek efficient and cost-effective ways to stay connected.
One revolutionary technology that has transformed the way we communicate is IP telephony. It has empowered remote teams to work on collaborative projects as well as allowed businesses to connect with international audiences.
Let us understand what an IP phone is and how it functions. Also, we will explore features, benefits, and challenges, as well as why it is a preferred choice for many.

To get the full benefits of an IP telephone system, connect it effortlessly with your CRM system. This integration enables automatic call logging, quicker customer data access, and increased personalization, eventually increasing engagement and efficiency in prospect management and deal closure.
What Is IP Telephony?
IP telephony (Internet Protocol telephony) refers to technologies that use various kinds of protocols to exchange voice, fax, and other types of information, which are often transmitted over the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
The call is transmitted in the form of packets through a Local Area Network (LAN) or the Internet, eliminating PSTN tolls.
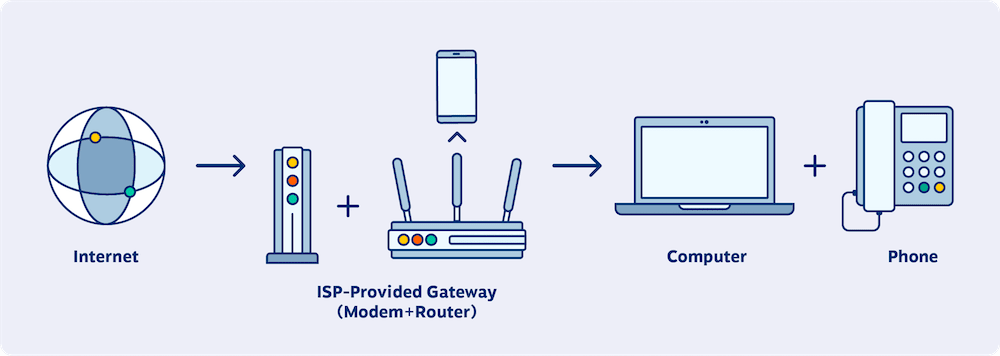
IP telephone system converts voice calls, faxes, and other information into digital signals. These digital signals are transmitted as data packets over IP networks, such as the Internet, via IP packet-switched connections.
IP Telephony vs VoIP
IP and VoIP telephone systems are commonly used interchangeably. However, there are some differences between them.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) refers to IP-based voice functionality such as voice calls and voicemail. It can be used to make and receive voice and video calls, instant messaging, and to exchange other kinds of data. Let’s learn how it differs from IP telephony.
| Aspects | IP Telephony | VoIP |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Specifically, it refers to the technology used to transmit voice communications over IP networks. | |
| Scope | Focuses solely on voice transmission. | |
| Infrastructure | It can be simpler sometimes only needs a VoIP adapter or software application. | |
| Quality of Service (QoS) | Call quality may vary depending on network conditions. | |
| Cost | Offers cost savings compared to traditional telephony, often with lower initial setup costs. | |
| Flexibility | Offers flexibility in voice communication but is limited to voice services. |
Both technologies have substantially revolutionized communication, providing cost reductions, enhanced functionality, and the ability to interact with people all over the world. Businesses and individuals can select the best choice for their communication needs and preferences.
Key Components of IP Telephony System
IP telephony systems have many components that work seamlessly together for effective communication. The key components of the IP telephone systems include:
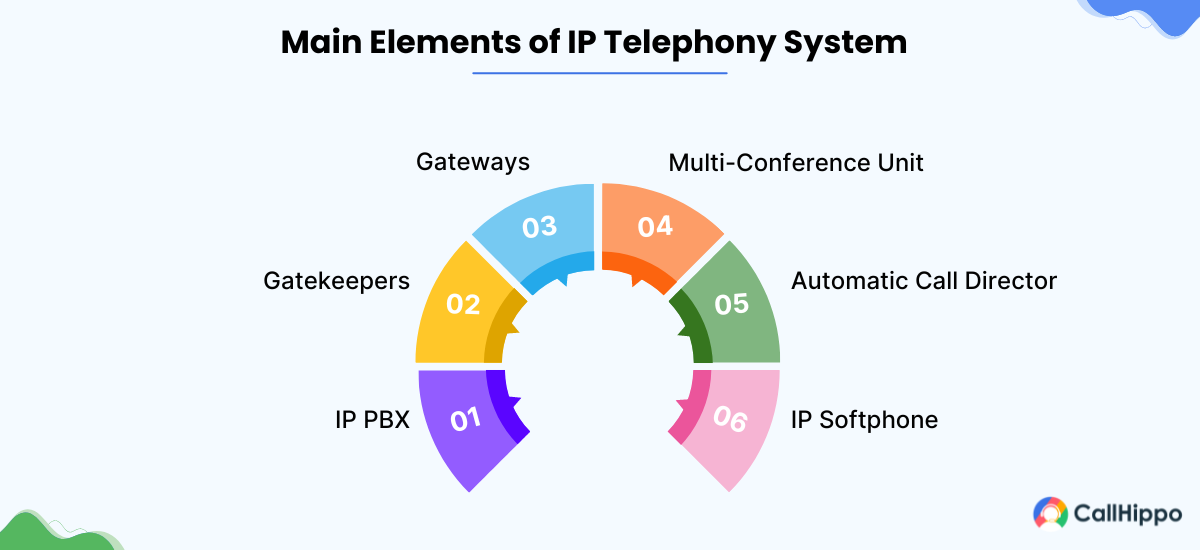
1. IP PBX (Private Branch Exchange)
An IP PBX (Private Branch Exchange) is a sort of phone system that uses internet protocols to manage and connect telephone extensions within a company or organization
It is a private telephone switch that lets the owner function as a mini-service provider for its subscribers, offering a variety of additional functions such as call transfer, call waiting, IVR (Interactive Voice Response), queues, reports, and more.
2. Gatekeepers
In an IP telephone system, the gatekeeper serves as the “traffic cop.” It routes calls between the system’s various endpoints, such as phone calls, gateways, and multi-conference units.
It also controls how devices use the network, prioritizing time-critical voice traffic while managing overall network utilization and ensuring quality of service.
Gateways also facilitate connectivity between IP telephony systems and the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, enabling real-time communication between interconnected devices and enhancing operational efficiency
3. Gateways
Gateways provide seamless connectivity between IP phones and other telephone systems, such as the traditional public telephone network and older PBX systems.
Gateways can also be used to “IP enable” a traditional PBX, which allows calls to be routed over the IP data network rather than the telephone network, lowering call costs. This “least call routing” also allows you to consolidate your telephone resources, which lowers administrative costs.
4. Multi-Conference Unit (MCU)
An MCU enables a large number of people to participate in a single audio or video conference simultaneously. It monitors the conference, determines who can attend, and allows a moderator to guide the conversation.
The MCU can transcode data streams, allowing devices with differing communications protocols or network speeds to communicate.
5. Automatic Call Director/Interactive Voice Response
Call centers and other high-volume applications demand extensive control over call routing. An automatic Call Director (ACD) holds calls for agents, prioritizing and routing them based on the caller and agent’s capabilities.
Interactive voice response (IVR) systems use voice prompts and user information to design calls, frequently accessing databases throughout the call. IP telephony technology enables the creation of complex applications while reducing operating expenses.
6. IP Softphone
A softphone is software that transforms your computer into a virtual phone. In addition to enhanced calling facilities and directory services, it often involves video calling.
Softphones use IP technology, which makes it easier to implement complex applications. For example, to dial a phone number, simply click on a name in your address book.
Challenges of IP Telephony
Despite the numerous advantages of the IP telephone, there are several challenges that one needs to be aware of. Some of these challenges are:

1. Server Latency
Server latency is a significant challenge in IP telephony systems, as it can cause delays in data transmission and affect the overall performance of the system. Additionally, server latency can also affect the overall user experience, as users may experience delays in receiving responses to their requests.
2. 911 Calls
Despite the Federal Communications Commission’s order that VoIP providers include 911 as a basic feature, callers must register their physical addresses with their providers. If they fail to do so, 911 VoIP calls may not offer accurate location and phone number information.
3. Power Requirements
Power requirement is a significant challenge for IP telephonic services, as they require reliable and consistent power to operate effectively. Power outages can cause IP telephone systems to shut down, resulting in lost productivity and revenue.
4. Port Problems
Port problems refer to issues that occur when IP telephone systems are unable to properly use or configure specific ports for data transmission. This can cause a range of problems, such as reduced network efficiency, security risks, and an increased error rate in data transmission, and can also cause poor call quality.
5. Jitter
Jitter is a common issue in IP telecommunication that can significantly impact call quality. It refers to the variation in the delay between successive packets of data transmitted over a network. This variation can cause the received data to arrive at the destination in a different order than it was sent, resulting in poor call quality and distorted audio.
6. Quality of Service (QoS)
Maintaining high-quality voice transmission can be challenging, especially during periods of high network traffic. QoS mechanisms must be in place to prioritize voice packets and minimize latency and jitter.
VoIP: The Smart Choice for Reducing Your Monthly Bills
VoIP technology is well-known for its cost-saving features, making it an appealing choice for both businesses and individuals. VoIP reduces the need for costly traditional phone lines and long-distance calls by utilizing the Internet for voice communication.
Platforms such as CallHippo offer competitive pricing plans with unlimited calling and additional features such as voicemail, call forwarding, and conferencing at no extra cost.
By CallHippo
- Smart DID Routing
- Automatic Call Distribution
- Call Center Analytics

Conclusion
To summarize, IP phones have changed the way we communicate, providing a plethora of features and benefits that regular phones cannot match. As businesses accept remote working and globalization, IP phones provide a dependable and cost-effective communication solution.
With ongoing technological advancements, the future of IP phones looks even more exciting, promising enhanced communication experiences for individuals and organizations alike.
FAQs
1. What is IP in telecommunication?
IP, or Internet Protocol, is a set of rules governing the format of data sent over the Internet connection or other networks. It allows devices to communicate by breaking data into packets and routing them to their destination.
2. What is IP and its types?
IP, or Internet Protocol, is a fundamental protocol used for routing data across networks. There are two main types of IP: IPv4, which uses 32-bit addresses, and IPv6, which uses 128-bit addresses, allowing for a larger number of unique addresses.
3. What are IP telephony applications?
IP telephony applications include VoIP calling, video conferencing, instant messaging, multimedia streaming, and unified communications, all of which leverage IP networks to provide seamless and cost-effective data communication services.

Subscribe to our newsletter & never miss our latest news and promotions.








