Call center technology has advanced significantly in the last decade, with many businesses relying on it to improve customer service. That’s because customer satisfaction is the name of the game, and businesses know that.
In fact, according to Forbes, 96% of customers consider customer service a factor in their choice of brand loyalty. The same study suggests that loyal customers are five times more likely to purchase or buy again and about four times more likely to refer your company to their friends—critical metrics of a good business.
As the industry progresses, there is an increasing focus on contact center automation, which promises even more efficient processes and better customer experiences and satisfaction. These exciting new call center technologies will improve contact center performance tenfold.
Read on and discover some trends, features, and future developments that you and your call center team can use to improve customer interactions and boost customer satisfaction.
"Advancement in IT has revolutionized the way businesses communicate with their customers. You can now effortlessly engage with your customers and prospects with a simple click. If you haven’t implemented a call center solution yet, it’s time to adopt the advanced call center technology and streamlining the communication process."
What is Call Center Technology?
Businesses utilize call center technology to enhance customer service by equipping agents with tools to effectively engage with and address customer needs via phone calls. They use and combine various technologies into a cohesive whole to ensure their customers are happy.
One such call center technology is voice over internal protocol (VoIP). It is the communication line between the call center agent and the customer. This technology allows you to receive and make phone calls using only an internet connection instead of an analog phone line.
As the years passed, more and more technologies were integrated into call center workflows — one of which is cloud computing. This technology allows call centers to cut the high costs of buying computer hardware and the real estate that houses these computers.
Last but not least is automation technology. Businesses can automate customer data analysis and behavior and identify which key areas of customer interactions to improve to provide a better customer journey. Some automation involves providing customers with product recommendations based on their journey with the brand.
Key Features of Call Center Technologies
Key call center technologies focus on improving customer interactions and boosting the overall customer experience. There is more to simply picking up the phone and answering customer inquiries. Here are some technologies that help contact centers provide premium customer support.
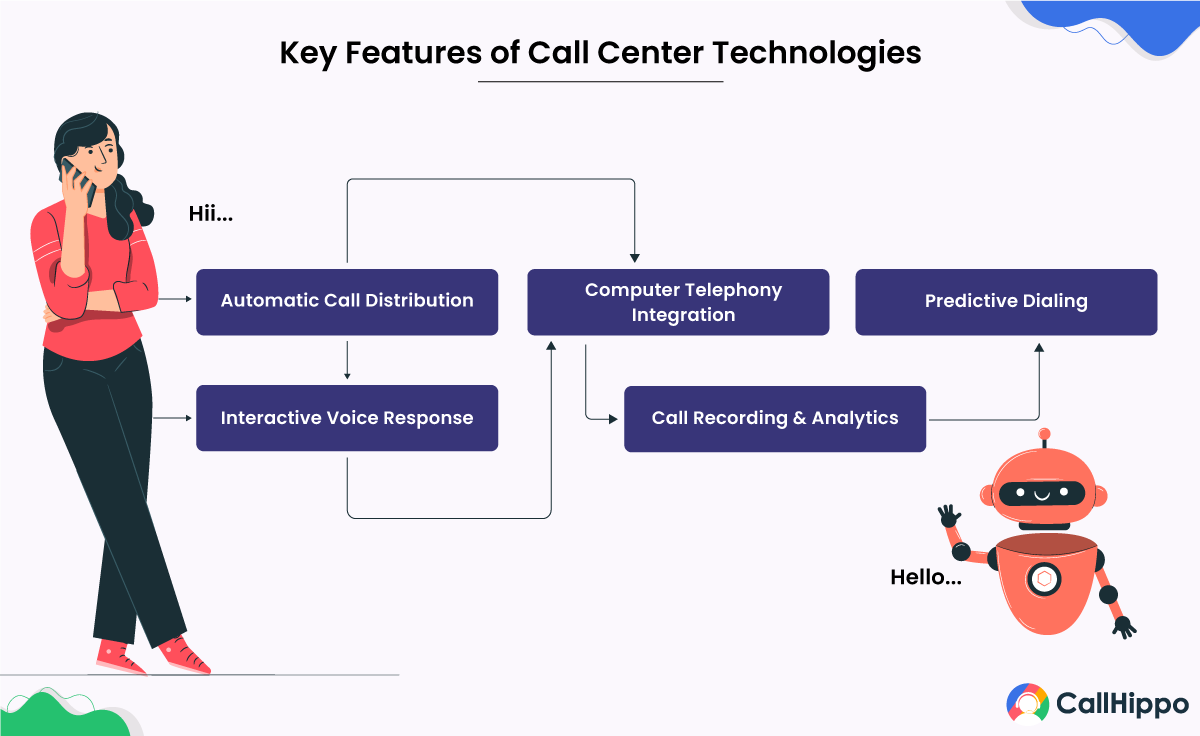
1) Routing calls with automatic call distribution (ACD)
Contact centers use automatic call distribution (ACD) to ensure customers can contact agents. This innovative call center technology helps route incoming calls to the most suitable customer service reps. It is an efficient way to manage calls and offers faster response times for customers. Call centers can scale their operations by automatically routing calls as call volumes increase or decrease.
2) Responding automatically using interactive voice response (IVR)
Interactive voice response (IVR) is another call center technology that allows customers to self-serve by providing pre-recorded answers to frequently asked questions. This automated call recording system lets customers quickly access the data or information they need without waiting for an agent. IVR is an ideal contact center technology that captures customer information and quickly provides the best possible customer service processes.
3) Multiple device integration using computer telephony integration (CTI)
CTI, also known as computer telephone integration, is an advanced call center technology that integrates the customer’s telephone and computer systems. This integration allows call centers to access customer data, provide faster response times, and make better decisions during calls, ultimately leading to a better customer experience.
4) Tracking customer service trends with call recording and analytics
Call recording and analytics are critical features of modern call center technology, allowing call centers to track customer service trends over time. With this technology, call centers can identify areas that need improvement and uncover opportunities for sales and marketing. The data and information collected can also improve the customer experience, enhance operational efficiencies, reduce costs, and improve the bottom line.
5) Maximizing contact rates by using predictive dialing
Predictive dialing is an efficient technology that helps call centers maximize contact rates and reduce the time spent on dialing by pre-selecting calls. This technology allows call centers to focus more on other aspects of the business. Predictive dialer is considered one of the most effective call center technologies.
Key Benefits of Call Center & Contact Center Technology
Customer service operations across industries face a recurring challenge: incoming calls accumulate faster than agents can address them. These agents spend considerable time navigating between five or six disparate systems to retrieve fundamental customer information. What should constitute a brief two-minute interaction frequently extends to ten minutes or longer, primarily because existing technology infrastructure fails to communicate effectively across platforms.
Organizations that successfully implement integrated technology solutions observe improvements in operational performance. Average wait times decrease in many cases. Agent retention improves noticeably, with fewer departures during the critical first three months. Operating expenses decline by approximately 30% or more across various implementations. The determining factor involves deploying systems that integrate cohesively and genuinely support operational workflows rather than impeding them.
1. Improved Efficiency & Agent Productivity
Observing contact center operations for several hours reveals persistent inefficiencies. Agents dedicate substantial portions of their workday to information retrieval rather than customer assistance. Customer relationship data resides in one system, while the knowledge base operates separately. Ticketing tools function independently. During this navigation process, customers remain on hold while their frustration builds incrementally.
Contemporary platforms address this fragmentation by consolidating essential functions. When an incoming call connects, agents immediately access customer interaction history, previous support tickets, relevant product specifications, and system-generated response recommendations within a unified interface.
You can improve efficiency and agent productivity by:
- Deploying smart call routing with skills-based assignment
- Implementing Automated Call Distribution (ACD) with real-time queue management
- using CRM integration for instant customer context
2. Personalized Customer Experience
Impersonal service delivery erodes customer trust with remarkable speed. Most consumers recognize the standard automated greeting: “Thank you for calling. Your call is important to us.” What typically follows involves twelve minutes of repetitive hold music while frustration mounts.
Advanced contact center technology fundamentally alters this dynamic. The system identifies returning customers, retains their documented interaction preferences, and modifies response approaches based on historical behavior patterns. It involves recognizing each customer as an individual with distinct needs and a documented history rather than simply another sequential ticket in the queue.
For a personalized customer experience, you can:
- Deploy an Interactive Voice Response (IVR) with custom caller recognition
- Use call whisper and screen pop for context-rich greetings
- Implement sentiment analysis for adaptive responses
3. Streamlined Omnichannel Customer Support
Consider a customer journey that occurs thousands of times daily: an individual initiates a chat conversation through a company website. When the chat remains unanswered or fails to resolve their concern, they follow up via email. Finally, mounting frustration drives them to telephone the support line. At each successive touchpoint, they must explain their entire situation from the beginning because organizational systems treat each communication channel as existing in complete isolation.
Genuine omnichannel technology eliminates this fragmentation. A conversation initiated through web chat appears within the same interaction timeline as subsequent email correspondence and telephone calls. Agents access the complete contextual history regardless of which channel the customer originally selected. Customers no longer repeat information across multiple interactions.
To streamline omnichannel customer support, you can:
- Create unified customer timelines across all channels
- enable channel switching without context loss
- Deploy chatbots with smart escalation to voice
4. Reduced Operational Costs & Scalability
Traditional call center infrastructure requires substantial capital investment. Expansion initiatives need new physical facilities, equipment procurement, and dedicated staff. Opening an additional location typically requires capital expenditures in the hundreds of thousands. Scaling operations to address seasonal demand fluctuations means hiring temporary personnel who face subsequent layoffs within three months.
Cloud-based contact center infrastructure eliminates most of these constraints. Organizations can augment capacity immediately without constructing new physical infrastructure. The financial model shifts to operational expenses that scale proportionally with actual utilization. Remote work arrangements become operationally viable, and that expands hiring pools beyond geographic limitations.
You can reduce operational costs and scalability by:
- implementing cloud-based systems with pay-as-you-go pricing
- deploying self-service IVR to reduce agent volume
- using remote agent capabilities to tap global talent
5. Better Data-Driven Decision Making
Call centers generate substantial volumes of interaction data throughout each operating day. Each conversation contains potentially valuable insights regarding customer requirements, product deficiencies, agent performance characteristics, etc.
Without appropriate analytical tools and systematic capture mechanisms, this information disappears. Supervisors make operational decisions based on intuition and the limited sample of interactions they personally monitor.
For making better data-driven decisions, you can:
- Implement real-time analytics dashboards for immediate action
- Deploy call recording with AI-powered transcription and analysis
- Use predictive analytics to forecast volume and optimize scheduling
6. Increased Agent Satisfaction & Lower Burnout
Annual agent turnover in call center operations averages between 30-45% across the industry. The financial costs associated with recruiting, hiring, and training replacement agents accumulate to thousands of dollars per position, not including the productivity losses during transition periods.
Burnout drives these turnover figures. To improve agent satisfaction and lower burnout, call centers can:
- Provide agent-assist technology that reduces cognitive load
- enable flexible scheduling and remote work options
- Implement gamification to recognize performance and create engagement
Emerging Call Center Technology Trends
The call center industry is rapidly evolving with the emergence of new technologies. Adapting to these newer technologies to stay competitive in this digital age would be ideal to avoid getting left behind. Here are some more exciting trends you should keep an eye on.
1. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence for call centers is a rapidly growing technology revolutionizing how businesses interact with customers. With AI, contact centers can automatically respond to customer inquiries by understanding natural language and providing tailored solutions.
Advanced AI capabilities allow businesses to gain deeper insights into customer service trends and make informed decisions. AI-powered analytics help companies optimize their operations and improve call center agents’ productivity.
2. Cloud computing
Cloud computing is an increasingly popular call center technology that enables call centers to store and access customer data anywhere. By leveraging powerful cloud-based tools, organizations can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and provide better customer experiences.
With cloud computing, companies have greater flexibility when scaling up or down, access to real-time data, secure cloud storage options, and improved customer support solutions. This helps them better serve their customers and compete in this highly competitive business landscape. ?
3. Remote work solutions
Remote work solutions are call center technology trends that have gained popularity since the pandemic. These call center software programs allow contact center agents to work from any location. This contact center technology enables organizations to reduce operational costs and improve employee productivity since employees can work independently without commuting to the office.
Additionally, remote work call center software provides businesses with enhanced analytics capabilities so that contact center managers can track call center agents’ performance in real-time and make better business decisions. Companies can also monitor agent compliance with customer service guidelines, ensuring a consistent customer experience. ?
4. Self-service options
Self-service options are becoming increasingly popular as a means of improving customer service. They allow customers to quickly and conveniently get answers to their inquiries without waiting for an agent. This call center technology is gaining popularity because it provides customers with a near-instant solution to their problems.
By automating everyday tasks such as FAQs and account setup, companies can reduce agent costs and provide a more efficient experience for customers. Self-service options enable customers to access information anytime, anywhere, making the experience more convenient and streamlined.
5. UCaaS + CCaaS Convergence
Internal communication platforms and customer service systems have historically operated as entirely distinct entities. Unified Communications as a Service managed internal team collaboration—chat functionality, video conferencing, and file sharing capabilities. Contact Center as a Service handled customer-facing interactions, calls, support tickets, and customer data management. Agents switched constantly between these separate platforms.
Platform convergence merges these previously separate functions. Agents can communicate with colleagues, bring supervisors into active customer calls, and reference knowledge base articles without departing from a single unified interface. Contextual information flows continuously rather than fragmenting each time agents transition between tools.
Business-to-business support operations demonstrate the advantages most clearly. Rather than transferring customers to specialized departments, which often involves hold time and repeated explanations, agents bring relevant specialists into ongoing conversations through internal messaging. Customers maintain continuity with a single point of contact while receiving expert assistance that remains invisible in the background. Resolution times decrease substantially under this model.
6. Mobile Optimization for Agents & Customers
Desktop workstations no longer define how business interactions occur. Customers browse products on mobile devices and initiate calls with questions while away from home or office environments. Field technicians require the ability to handle customer calls between on-site appointments. The assumption that all participants operate from fixed desk locations has become outdated.
Mobile-optimized platforms provide complete functional capability across devices. Customers can initiate chat conversations, verify order status, or place calls through mobile applications. Agents can manage interactions using tablets or smartphones without sacrificing features available on desktop systems.
Field service organizations observe the most direct operational benefits. Technicians address customer questions immediately from job sites rather than deferring responses until returning to office facilities. First-call resolution rates improve because the individual with the most relevant contextual knowledge can engage directly and immediately.
7. Contact Center as a Profit Center
Most finance departments categorize call centers as necessary cost centers that reduce overall organizational profitability. Traditional success metrics emphasize minimizing per-interaction costs. Each customer call represents an expense line item on financial statements.
Progressive organizations are reframing this traditional perspective. Customer interactions present opportunities to upsell additional products or services, prevent customer churn, and gather product improvement feedback that enhances future offerings. The contact center transitions from a pure cost center to a potential revenue-generating engine.
Technology infrastructure enables this operational transformation. Systems identify upselling opportunities by analyzing customer profiles and purchase histories. They provide agents with contextually relevant product suggestions at appropriate moments. They track revenue generated per interaction alongside costs incurred, enabling more nuanced performance evaluation.
Software-as-a-Service companies have embraced this model with particular success. When customers on basic subscription tiers ask questions about premium features, the system prompts agents with relevant upgrade information. A notable percentage of support conversations conclude with sales transactions that would not have occurred without this systematic approach.
8. Internet of Things (IoT) Enabled Proactive Service
Connected devices produce continuous data streams reporting operational status. Security cameras transmit functionality indicators. Industrial equipment monitors its own performance characteristics. Medical devices track patients’ vital signs. This information flows constantly to the monitoring infrastructure.
Forward-thinking companies leverage this data stream for proactive service delivery. Rather than waiting for customers to recognize problems and initiate complaint calls, contact centers place outbound calls first. “Our monitoring systems indicate your camera went offline approximately 15 minutes ago. Let’s troubleshoot that together.”
Home security companies integrating call centers with IoT systems find that when cameras go offline, automatic outreach calls reach customers before they notice problems. Satisfaction scores increase because customers feel cared for rather than reactive.
9. API-First Architecture & Custom Integrations
Every organization operates with a unique combination of software platforms. Customer relationship management systems might be Salesforce, HubSpot, or proprietary systems developed internally. Billing platforms, inventory management tools, and marketing automation all require data exchange with contact center infrastructure.
Traditional contact center platforms provide limited integration options with major software vendors. Connecting non-standard systems requires expensive custom development work or simply proves infeasible within technical and budgetary constraints.
API-first architecture fundamentally changes this limitation. Every platform feature exposes an application programming interface. Development teams can connect whichever systems matter to specific business requirements without depending on vendor roadmaps for each integration need.
Healthcare networks illustrate the possibilities this architecture enables. Patient management systems integrate with contact centers through APIs. Complete medical histories appear automatically when patients initiate calls. Following call completion, agent notes synchronize back to patient records without manual intervention. Data entry never occurs twice.
10. Security, Compliance & Ethical AI
Contact centers process highly sensitive information continuously throughout each operating day. Credit card numbers, health records, social security numbers, and personal identifiers all flow through the system infrastructure. This creates substantial risk exposure.
Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and CCPA impose strict requirements. Non-compliance triggers massive fines and legal liability. AI introduces new ethical concerns. Biased algorithms, opaque decision-making, and customer manipulation risks all need safeguards.
Modern contact center technology builds security, compliance, and ethical AI into core functionality. Encryption protects data in transit and at rest. Compliance features automatically redact sensitive information. AI transparency features explain automated decisions.
Financial services organizations frequently select platforms based primarily on compliance capabilities. Automatic redaction ensures agents never view complete credit card numbers during customer interactions. Recording systems mask sensitive data before storage. Comprehensive audit trails document all data access events. Organizations consistently pass regulatory audits without compliance violations when these systems function properly.
11. Agent Assist Features
Self-service channels increasingly handle straightforward customer inquiries. This progression leaves agents managing complex issues that require expert-level knowledge across numerous subject areas simultaneously.
Traditional training approaches involved months of intensive learning before agents achieved competent performance levels. Knowledge bases provided some assistance, but agents still needed to understand what information to search for and where to locate it within extensive documentation.
Agent assist technology delivers real-time guidance during customer conversations. AI systems monitor calls and surface relevant knowledge base articles, response scripts, or suggested solutions. New agents access expert knowledge without spending months memorizing extensive documentation that may become outdated.
Software companies implementing agent assist capabilities report new hire ramp times decreasing from approximately three months to four to six weeks. First-call resolution rates for inexperienced agents approach those of veteran staff members significantly faster than traditional training methods achieve.
12. Automated Quality Management (AQM)
Manual quality monitoring samples tiny fractions of actual interactions. Supervisors review a handful of calls per agent monthly from thousands handled.
This creates inconsistent feedback. Quality issues go undetected for weeks. Coaching focuses on whatever calls happen to get reviewed rather than systematic patterns.
Automated Quality Management analyzes 100% of interactions using AI. Systems score calls against quality criteria automatically. They identify coaching opportunities, compliance gaps, and performance trends.
Healthcare call centers using AQM discover compliance issues that manual sampling misses. Targeted coaching eliminates these gaps quickly. Quality scores improve dramatically because every interaction receives evaluation rather than random samples.
13. Voice Biometrics & Identity Verification
Identity verification wastes time and frustrates customers. “For security purposes, please verify your account number, billing zip code, and last four of your social security number.”
Customers repeat this process every call. High-security environments require even more verification steps. Voice biometrics authenticates customers using voice patterns. Unique vocal characteristics verify identity in seconds. Customers say a simple phrase, and the system confirms identity.
This eliminates security questions while improving actual security. Fraudsters can steal answers to security questions. They can’t replicate someone’s unique voice patterns.
Banking institutions implementing voice biometrics see average call time drop significantly. Customer satisfaction increases specifically related to call efficiency. Fraud attempts decrease because criminals can’t bypass voice authentication.
14. Conversational AI
Chatbots and IVR systems traditionally followed rigid scripts. “Press 1 for sales. Press 2 for support.” Customers navigated frustrating menu trees.
Conversational AI understands natural language. Customers speak or type normally. Systems comprehend intent and respond appropriately.
This technology combines natural language processing, machine learning, and dialogue management. AI interprets what customers actually mean, not just the keywords they use.
E-commerce companies replacing menu-based IVR with conversational AI see containment rates improve substantially. Customers resolve simple issues faster, while complex problems reach agents with clear context about what customers have already tried.
What are the Different Types of Call Center Technologies?
Call centers serve different purposes. Customer service departments handle incoming questions. Sales teams make outgoing calls. Some operations do both.
Each function requires different technological capabilities. The right tools depend entirely on what you’re trying to accomplish.
1. Inbound Call Center Technology
Inbound centers receive calls from customers. Questions about orders, technical support requests, billing inquiries, and general information needs.
Technology priorities focus on intelligent routing, minimal wait times, and complete customer context. You need systems that connect customers to the right agent quickly while providing that agent with everything they need to help.
- Automatic Call Distribution (ACD): Routes incoming calls to available agents based on skills, availability, and business rules. Intelligent ACD uses algorithms that consider agent expertise, current queue depth, and customer priority to optimize every connection.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR): Greets callers and routes them to appropriate departments or provides self-service options. Modern IVR includes natural language processing so customers can speak naturally instead of navigating numbered menus.
- CRM Integration: Displays complete customer history when calls connect. Integration with platforms like Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho shows purchase history, previous interactions, open tickets, and account details automatically.
- Call Recording: Captures conversations for quality monitoring, training, and compliance. Advanced systems include searchable transcriptions and automatic quality scoring.
2. Outbound Call Center Technology
Outbound centers make calls to customers or prospects. Sales calls, appointment reminders, survey collection, and proactive support outreach.
Technology priorities shift to dialing efficiency, contact rate optimization, and compliance management. You need systems that maximize productive conversations while adhering to calling regulations.
- Predictive Dialer: Automatically dials multiple numbers per agent, connecting only when someone answers. Algorithms minimize agent idle time while respecting abandonment rate regulations.
- Power Dialer: Dials one number per agent automatically, moving to the next immediately after call completion. This maintains steady pacing for sales teams focused on quality over quantity.
- Preview Dialer: Shows agents’ customer information before dialing, letting them prepare for each conversation. Agents typically get 10-30 seconds to review profiles before calls connect.
- Compliance Management: Ensures adherence to TCPA, Do Not Call lists, and calling time restrictions. Systems automatically scrub lists against DNC registries and prevent calls outside permitted hours.
3. Blended Call Center Technology
Blended operations handle both inbound and outbound calls. Agents switch between answering customer calls and making proactive outreach.
This approach maximizes agent productivity during slow inbound periods. When queues are empty, agents make outbound calls. When inbound volume spikes, systems pause outbound campaigns and reallocate agents.
- Intelligent Workload Balancing: Automatically adjusts agent assignments between inbound and outbound based on real-time demand. Systems monitor queue depth and dynamically move agents where they’re needed most.
- Campaign Prioritization: Manages multiple outbound campaigns while ensuring inbound service levels stay within targets. Campaign managers pause low-priority outbound calls when inbound queues exceed thresholds.
- Unified Agent Interface: Single desktop application for both inbound and outbound work. Agents handle any call type using one interface, eliminating system switching.
- Blended Performance Metrics: Tracks productivity across both functions accurately. Dashboards show inbound metrics, outbound metrics, and blended efficiency measurements.
What Challenges Do Call Centers Face with Technology?
Technology solves problems but also creates new ones. Implementation challenges, integration headaches, and adoption struggles derail many initiatives. Understanding common obstacles helps you avoid them or minimize their impact:
1. System Integration Issues
Call centers already operate multiple systems before introducing new contact center technology. Customer relationship management platforms, ticketing tools, billing systems, and knowledge bases all contain essential data that new platforms must access to function effectively.
When integration implementation fails or requires manual workarounds, agents waste considerable time switching between system interfaces and entering duplicate data across platforms. Many technology vendors advertise seamless integration capabilities, but deliver basic API access requiring expensive custom development work to achieve functional integration.
Solution: Choose platforms with pre-built integrations for your existing tools. Test integrations during proof-of-concept periods. Verify that data flows bidirectionally and updates happen in real-time. Ask about field mapping flexibility and whether professional services fees apply.
2. High Call Volumes
Unexpected volume spikes overwhelm systems and agents. Product launches, marketing campaigns, service outages, or viral social media posts can triple normal call volume in hours.
Systems crash under load. Queues explode. Customers abandon calls. Agents panic under pressure. Traditional solutions involve overstaffing for potential spikes, which wastes money during normal periods. Or accepting poor service during peaks, which damages customer relationships.
Solution: Cloud-based systems scale automatically. They handle volume spikes without performance degradation. Combine this with overflow routing that redirects calls to backup teams or offers callbacks when wait times exceed thresholds.
Modern IVR deflects simple inquiries to self-service during peak periods. “Our current wait time is 12 minutes. Press 1 to check your order status online, or stay on the line to speak with an agent.
3. Agent Burnout
High-stress environments, difficult customers, repetitive tasks, and inadequate tools drain agents emotionally and mentally. Burnout leads to absenteeism, poor performance, and turnover.
The cycle perpetuates itself. Burned-out agents quit. Remaining agents handle heavier workloads. More burnout. Understaffing makes everything worse.
Traditional responses include motivational speeches and pizza parties. These don’t address root causes.
Solution: Technology reduces burnout by eliminating frustrating elements. Unified interfaces stop agents from system-hopping. Agent assist reduces cognitive load. Better routing matches agents to appropriate calls rather than random assignments.
Flexible scheduling and remote work options improve work-life balance. Gamification creates engagement. Real-time performance visibility helps agents see their impact and progress.
4. Data Security Concerns
Call centers handle sensitive information. Credit card numbers, social security numbers, health records, and personal identifiers flow through systems daily.
Security breaches expose companies to regulatory fines, lawsuits, and reputation damage. Data breaches can cost companies millions.
On-premise systems put security responsibility entirely on your team. You manage encryption, access controls, patch management, and threat monitoring. Few call centers have expertise for enterprise-grade security.
Solution: Enterprise cloud platforms handle security as a core competency. They employ dedicated security teams, maintain compliance certifications, and implement multiple layers of protection.
Look for SOC 2 Type II certification, which verifies security controls through independent audits. Ensure end-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest. Verify compliance features for regulations that apply to your industry—PCI DSS for payment cards, HIPAA for healthcare, and GDPR for European customers.
Role-based access controls ensure agents see only the data they need. Automatic PCI redaction masks credit card numbers in recordings and screens. Audit logs track every data access for compliance verification.
5. Poor Customer Experience
Technology should improve customer experience, but poorly implemented systems make things worse. Confusing IVR menus. Disconnected omnichannel experiences. Agents without proper customer context. Long wait times despite advanced routing.
Customers judge your company by their support experience. They share positive experiences with several people. But they share negative experiences even more.
Solution: Design technology implementation around customer experience, not just operational efficiency. Map actual customer journeys. Identify friction points. Test systems from the customer perspective before full deployment.
Simple IVR menus with natural language options reduce frustration. Unified omnichannel platforms let customers switch channels without repeating information. Skills-based routing connects customers to qualified agents faster. Real-time analytics help supervisors maintain service levels.
Most importantly, give agents the tools and authority to actually solve problems. Technology that empowers agents improves customer experience more than any automated system.
Conclusion
Call center technology fundamentally reshapes how business organizations communicate with their customer base. Appropriately selected and implemented systems reduce operating costs, improve operational efficiency, and create substantially better experiences for both customers and agents.
Cloud-based platforms have become dominant in the market because they scale effortlessly to accommodate demand fluctuations and eliminate physical infrastructure management burdens. Artificial intelligence handles routine tasks while guiding agents navigating complex problem-solving situations. Omnichannel capabilities engage customers through their preferred communication channels rather than forcing them into specific interaction modes.
Test thoroughly before committing. Run proof-of-concept trials with real agents handling actual customer interactions. Verify integrations work as promised. Confirm that training requirements fit your timeline and budget.
CallHippo delivers call center capabilities through an intuitive cloud platform. Companies get intelligent routing, omnichannel support, CRM integrations, analytics, and compliance features without complex implementations or massive budgets. The system works for teams of 5 or 500, scaling as your business grows.
FAQs
1. What are the technologies in call centers?
Call centers use various cutting-edge technologies to ensure their operations are more efficient and improve customer service. Here are a few of the game-changers:
- AI provides contact centers with automated responses to customer inquiries by understanding natural language and providing tailored solutions.
- Cloud Computing allows contact centers to store and access data remotely, while remote work solutions allow agents to work from anywhere.
- Advanced analytics provide companies with enhanced insights into customer behavior.
- Self-service options enable customers to quickly and conveniently get answers to their queries without speaking to an agent. ?
2. Why is technology important in call centers?
Technology is essential in a call center, enabling businesses to provide better customer experiences. It helps them reduce operational costs, improve efficiency, and track employee performance in real-time.
3. What equipment is needed to start a call center?
When starting a call center, you must have a computer or laptop, phone systems, headsets, and software. These components allow agents to manage and receive calls from customers. Other necessary equipment includes:
- A fast and reliable internet connection.
- A reliable power source.
- Customer relationship management (CRM) software.
These are just for starters. You will need more equipment to ensure the operational efficiency of your call center.
4. How much is it to own a call center?
Owning a call center can be a significant financial investment. The exact operating cost depends on many factors. This includes the size of the call center, types of equipment, and the number of agents. Essential equipment such as computers, phones, headsets, power supplies, and software can cost around $2,000 to $5,000.

Subscribe to our newsletter & never miss our latest news and promotions.








