What is ISDN? This question is intriguing as it is given that we’re headed to its switch-off in 2025, as announced by BT telecom providers back in 2015. Let’s roll back in time to understand this better.
The traditional landline technology was outdated and needed to be replaced with something more adaptable to the developing digital infrastructure. ISDN did so easily. It relied on copper lines to move the landline technology to digital infrastructure. ISDN connections were better, cheaper, and faster. So, where’s the catch?
Well, ISDN’s digital infrastructure cannot compete with broadband internet connection speeds anymore. As a result, ISDN has become obsolete and is being phased out by BT, eventually leading to its switch-off.
In this blog, we’ll discuss everything about ISDN. We’ll also elaborate on VoIP and SIP—technologies that have efficiently replaced ISDN, and why you are missing out if you haven’t switched already.
What is ISDN?
If you’re wondering what does ISDN stand for, it’s Integrated Services Digital Network.
ISDN, a circuit-switched telephone network system, transmits data and voice over digital lines (could be copper lines). These digital lines were introduced as a technical standard to revolutionize the outdated Public Switched Telephone Network.
ISDN’s design philosophy aims to offer end-to-end digital functions with better speeds, greater reliability, and higher quality than a classic telephone system. Basically, ISDN aimed to group all digital transmission services and offer them through a single user interface.
This set of communication standards uses digital transmission for data, voice, and signaling.
"There’s no reason to continue relying on a technology deemed obsolete and headed to a total switch-off in less than 2 years. It’s no longer a choice but a necessity to switch to advanced, updated, and more reliable solutions. VoIP checks off all the requirements and has proven its mettle with its cost-effectiveness, remote accessibility, portability, scalability, and new-age features. It’s time to choose a reliable VoIP service provider; the faster, the better."
What Are The Types Of ISDN?
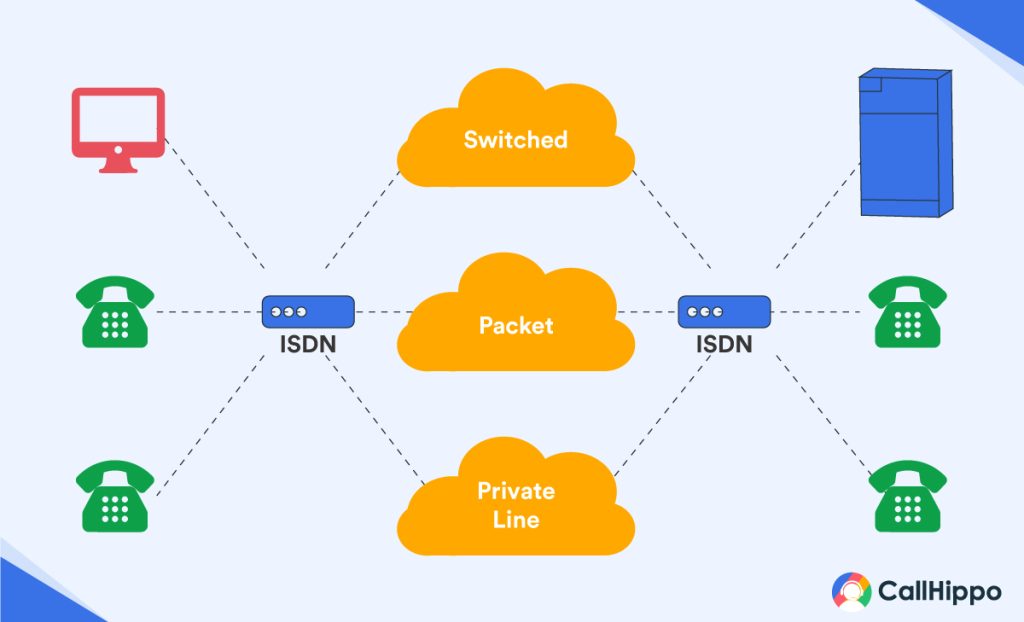
Integrated Services Digital Network or ISDN services primarily aim to accommodate a bouquet of digital transmissions into a single interface. There are 3 types of ISDN networks that offer different ISDN services.
Let’s look at these different ISDN interfaces:
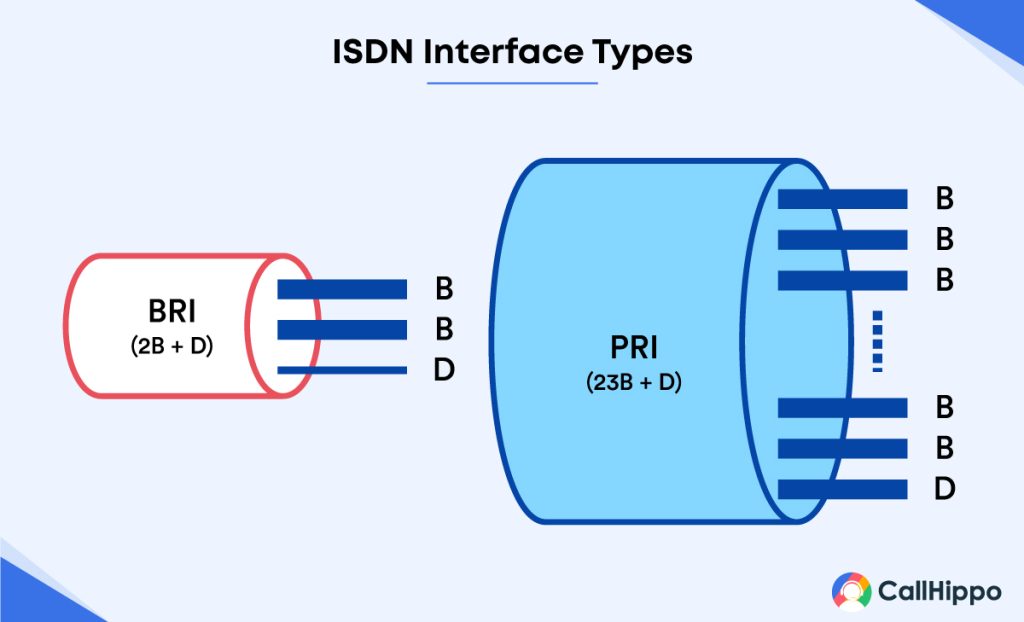
1. BRI (Basic Rate Interface)
The Basic Rate Interface, or BRI ISDN, has two data-bearing channels called the two B channels. However, it only has one signaling delta channel, the D channel, to initiate the connections. The channels are mutually exclusive and work independently of each other.
Looking at the more technical aspects, the two B channels have a maximum operating capacity of 64 kbps/channel. In comparison, the D-channel is limited to 16 kbps, which means the Basic Rate Interface (BRI) works at a speed of 144 kbps. In addition, it requires extra 48 kbps of operating overhead, bringing the total up to 192 kbps.
The B channels carry voice and user data due to higher bandwidth, while the D channel combines data, packet networking and control, and signaling. Both these ISDN channels are used to transmit information.
2. PRI (Primary Rate Interface)
Like ISDN BRI, Primary Rate Interface (PRI ISDN) has one D channel. However, it contains 23 or 30 B channels depending on your country. These D channels can transmit and receive data at 64 kbps. Adding 64 kbps of all 23 B channels and 8 kbps of overhead gives you a total transmission speed of 1.544 Mbps.
The main use of PRI (Primary Rate Interface) is to carry data between the user and the ISDN network.
As for their use case, PRI is used by enterprises and large corporations, while small businesses and residential areas use ISDN BRI.
3. B-ISDN (Broadband ISDN Line)
B-ISDN is the latest interface of ISDN. It is designed for the current business communications infrastructure and includes fiber optic cables. The entire ISDN can work without any reliance on copper cables. It is a service that requires transmission channels capable of supporting speeds greater than PRI.
The best way to do it is through fiber optics, as increasing the number of B channels only increase the dependency on existing infrastructure.
You May Also Read : Virtual PBX Phone System: Definition & Benefits
How Does ISDN Work And How To Setup ISDN?
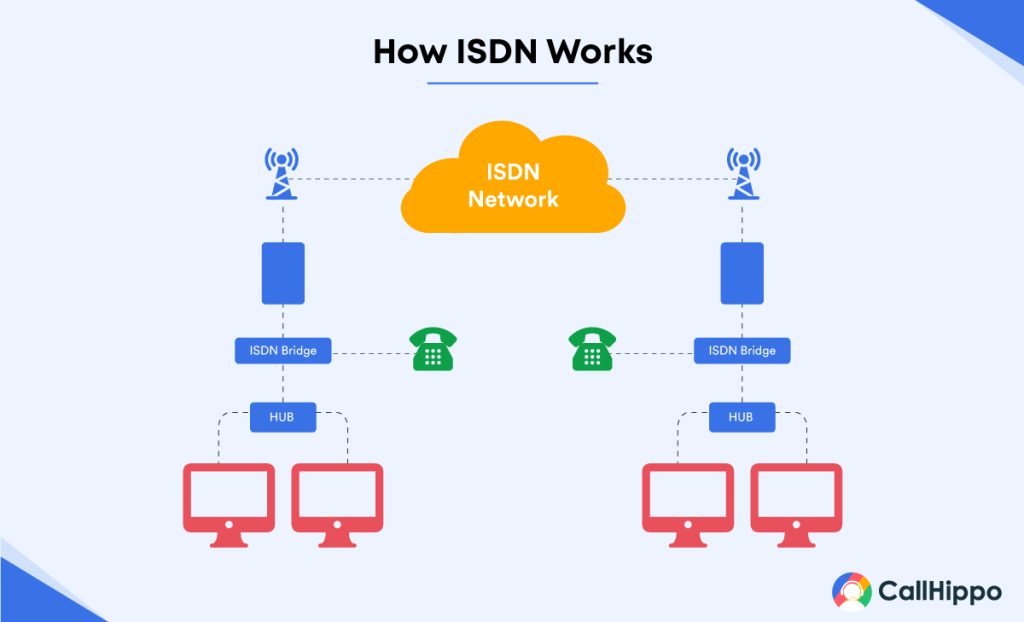
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) commonly helps users connect to the internet in areas where standard connections, like cable modems or DSL, are unavailable. Setting up an ISDN connection is easy and does not involve a lot of complex steps. You’ll be able to complete most of the setup process with your internet service provider (ISP). And the remaining steps can be easily done from home.
Follow these steps to set up an ISDN service:
Step 1: You require a working Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) line.
Step 2: Check your serial ports
Step 3: Load the modem driver disk onto your system
Step 4: Then, program the digital modem
Step 5: Connect the modem with the appropriate phone number
Step 6: Set your desired connection speed for the different phone lines
Step 7: Dial your ISP-assigned number through your modem
Step 8: Set your modem for BONDING if you can’t access a high-speed internet connection. BONDING allows the modem to dial up both numbers simultaneously.
The process is tedious and cumbersome. And the efficiency of the setup relies on existing physical infrastructures. Any small errors and glitches in any system can upset your internet access. One of the reasons, the ISDN process is getting phased out.
What Are The Alternatives To ISDN?
Businesses require faster and more reliable connections for calls with lower setup requirements. This gave rise to the need for ISDN alternatives. There are currently two alternatives to ISDN–VoIP and SIP.
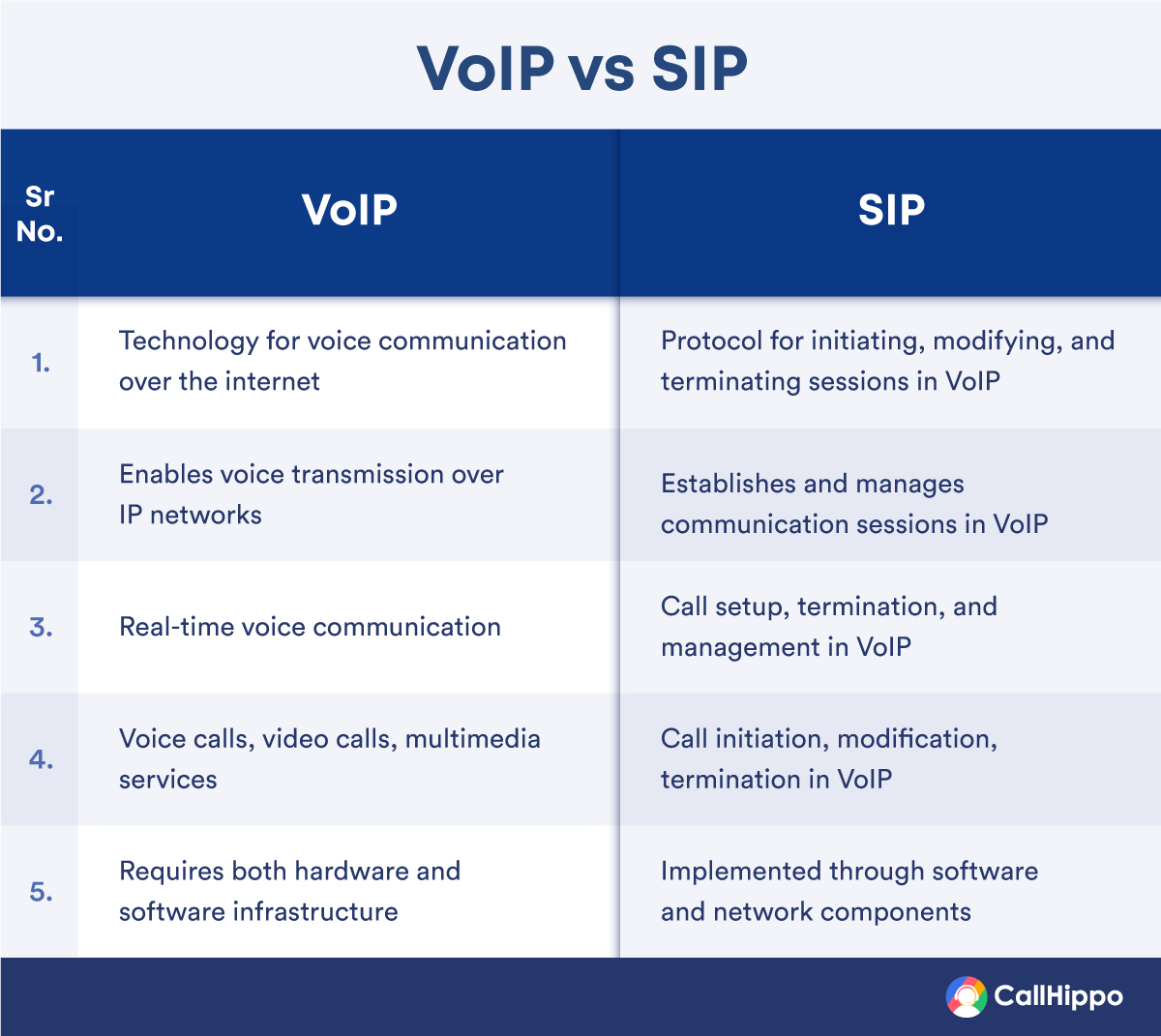
1. VoIP
Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is the best alternative for enterprises and businesses looking to replace their existing ISDN service.
In a nutshell, VoIP converts audio signals into digital transmission data. This data is sent over to the receiver via an internet connection. The lack of on-premise hardware and reduced reliance on existing traditional telephone infrastructure makes it an attractive upgrade.
Scaling your company is also easier as the bandwidth available for dialing and receiving calls can be increased on demand. Furthermore, employees enjoy the same user experience irrespective of location and device.
2. SIP
SIP, or Session Initiation Protocol, is another alternative to ISDN. But it lacks some of the features that VoIP offers.
SIP allows the business phone systems to access the network using the existing broadband connection, private circuit, or ethernet. SIP allows businesses to share messages, large files, videos, and other data formats across broadband.
The system can be configured to provide network access to multiple employees. The communication channel that connects one point to another is called the trunk. For this reason, the process is known as SIP trunking.
Even though SIP has an initiation protocol, it is regularly used to support other VoIP technology.
You May Also Read : Cloud-based vs. Traditional Telephony System
How to Switch from ISDN to Hosted VoIP?
The ease of installation of VoIP is responsible for increasing its user base from 6.2 million to 41.6 million in 8 years. It is hence easy to see why you must consider switching to hosted VoIP communications.
The switch from ISDN in a computer network to VoIP happens in two phases: planning and preparation and the final switch to VoIP.
1. Planning and preparation
The planning and preparation phase involves identifying your business goals, budgeting, and finding the right technology partner. Let’s look at them in detail.
Business Goals
Before deciding on the switch, ensure that your business goals align with your VoIP switchover plan. Identify the factors influencing your decision to switch.
For example, if you are only switching to avoid the ISDN switch-off, you will be better off going with a simple VoIP service provider. But, if you want cost savings, remote accessibility, total portability, greater scalability, and advanced features like call transfer and auto attendants, find a more robust and advanced VoIP provider.
Budget
After your business goals, you must fix your budget. Now, the budget can vary wildly depending on the deployment of your VoIP. Since cloud-based systems are hosted directly in the cloud servers, they are your most affordable option.
Finding the right technology partner
After deciding the budget and business goals, it is time to choose the right tech partner. VoIP providers’ tech stack and business infrastructure will vary depending on their offerings.
Try finding a partner with experience helping companies in your domain. In addition, ensure that your vendor is prompt, offers 24/7 customer support, understands your needs, and is equipped with updated features to match your requirements. You can even ask for trials before zeroing in.
2. Switching to VoIP
Once the hard part of strategizing is over, switching to VoIP is fairly simple. Here’s what you need to consider.
Access new features
Unlike traditional phone systems, VoIP serves you with a host of new-age features essential for you to remain competitive. You can access features like call queuing, conferencing, forwarding, bridging, and merging.
Connect the system with your hardware
With VoIP, you don’t need dedicated hardware as it utilizes the internet to function, providing complete location independence. The VoIP can connect to Bluetooth speakers, desk phones, Bluetooth headsets, and VoIP softphones.
Train your staff
Provide training modules to your employees to educate them on the newly deployed system. The right VoIP provider will provide enough resources to update your employees about the VoIP system. But you do not need to worry here, as 67% of employees find handling calls via VoIP systems far easier.
Install VoIP Business phone system
The VoIP provider also provides VoIP phone systems to offer your employees easier access to the network. Installing small business phone systems entails only plugging in the phones in the right places. However, setting up enterprise VoIP with multiple switches will take significantly longer.
You May Also Read : What’s a PBX System? Types, Features, Benefits
A Comparison Of ISDN Service and VoIP Systems
Having discussed how to switch to VoIP, it’s critical to discuss whether the switch from ISDN to VoIP is worth it. Let’s look at a few key differences to help you decide.
Factors | VoIP(Voice over Internet Protocol) | ISDN(Integrated Services Digital Network) |
| Reliability |
|
|
| Form |
|
|
| Flexibility |
|
|
| Pricing |
|
|
| Futureproofing |
|
|
Find out an in-depth elaboration on cloud-based vs. traditional phone system.
Why Switch From ISDN to VoIP?
It is evident from the differences that VoIP performs far better than ISDN. Here’s a closer look at the benefits of switching to VoIP from ISDN.
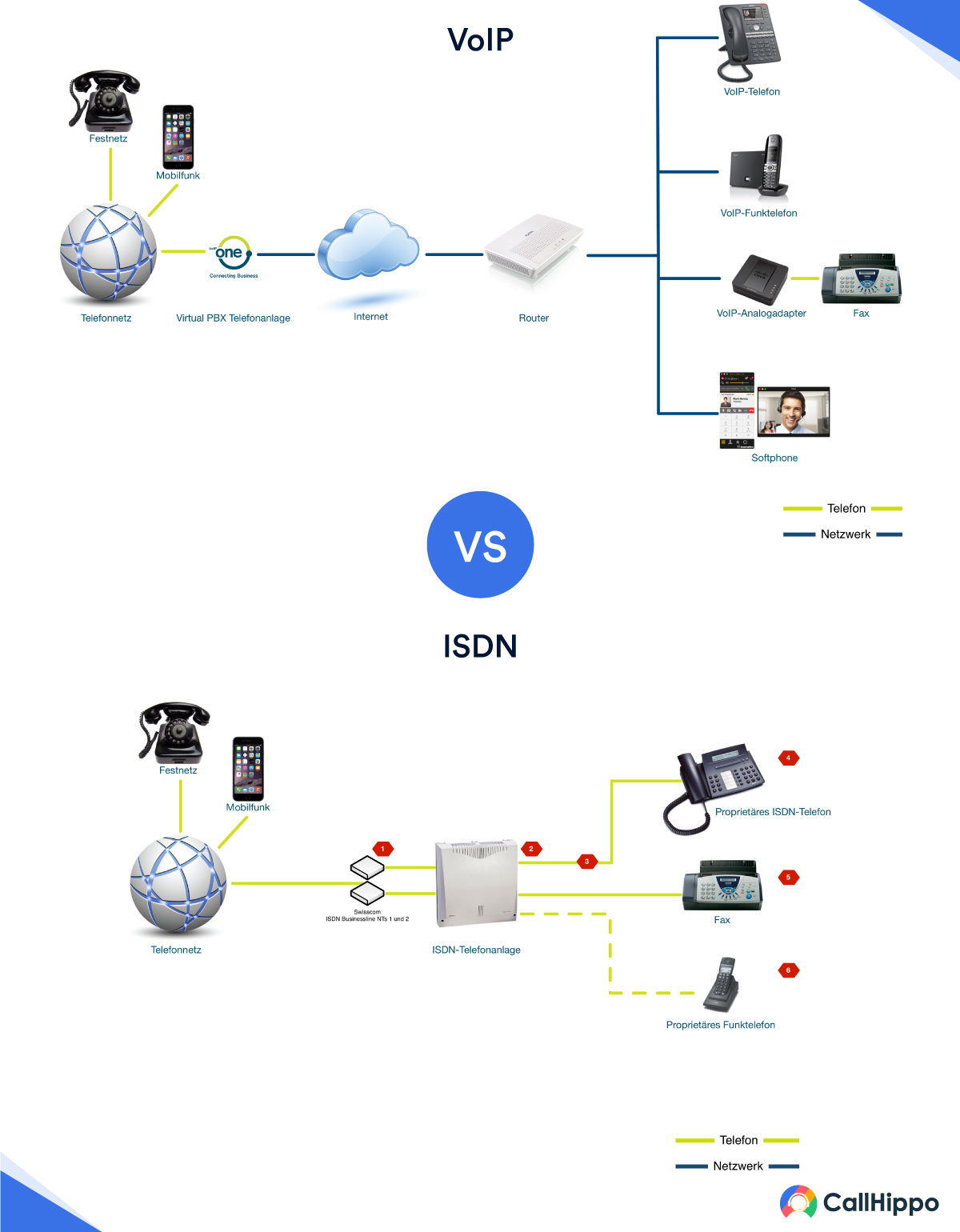
1. Increased accessibility
The VoIP systems can make calls from anywhere as long as you are connected to the internet. Your employees just have to use an ID and password to access VoIP. The system then connects to the internet, enabling them to make unlimited calls.
Remote employees use VoIP to connect to their business phones from anywhere in the world. VoIP call software is definitely essential for remote-first organizations.
2. Reduced cost
VoIP is sought after by businesses looking to increase their profitability. In fact, startups are known to save 90% of their starting-up costs with VoIP.
Implementing the landline phone system costs $50 per line. And international costs are more than that. On the other hand, VoIP only costs $20-30 per user/month, reducing call costs by more than 50%.
The initial setup cost of VoIP is high. But, in the long run, the reduced call costs significantly increase the ROI.
3. Enhanced scalability
Adding new lines in traditional ISDN-powered telephones is challenging. You need to contact the service provider and ask them to add new lines, leading to time and cost drainage. The long setup time presented a significant hurdle for fast-scaling businesses.
VoIP solves this issue with ease. Setting up new lines in VoIP is as simple as registering a new account in the system. The new connection attaches to any device and takes only a few minutes to activate.
This lack of friction makes onboarding new employees hassle-free, enhancing scalability.
4. Better control and credibility
Controlling the call quality and displaying credibility with traditional landlines is difficult. For example, with ISDN, employees only have access to local ISDN numbers. It makes it impossible to make legitimate international calls. Even if they get access to international markets, the cost of international calls makes the entire contraption unfeasible.
With VoIP, you’re free to choose the numbers for your specific international markets. VoIP also allows the organization to set up auto-attendants, which extends the reputation of a large and well-managed business. This fosters trust and improves customers’ relationships with the brand.
5. Improved voice quality
Traditional phone lines have excellent call quality. But the quality falters when you are making international calls. VoIP can maintain consistent call quality with a stable internet connection.
6. Additional features
VoIP also has several features that are missing from traditional ISDN telephone lines to improve business communications. Here are the top ones:
- Call waiting
- Call queuing
- Call forwarding
- Voicemail
- Caller ID
- Call conferencing
- Video conferencing
- Unified communications
Most VoIP service providers offer these features for no additional cost.
How To Switch From ISDN To SIP?
If you are not going with VoIP, opting for SIP trunking is also a viable option for replacing your ISDN-based telephone line. Below, you will find all the essential steps to switch from ISDN to SIP.
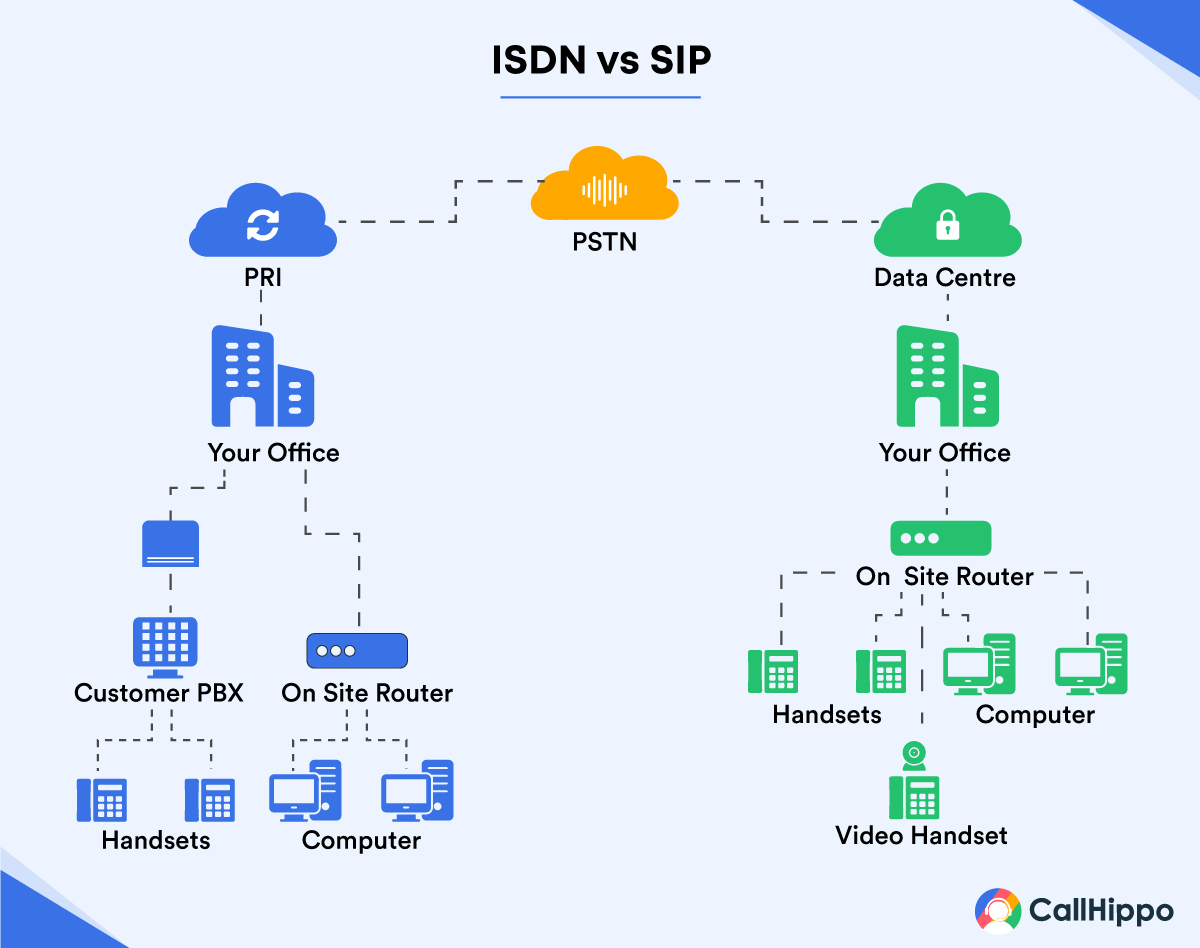
1. Understanding the problem
Discuss with your communication teams and understand the problems with your existing ISDN system. Next, you can replace the system phase-wise or the entire software in one go.
One of the advantages of SIP trunking is that it can work simultaneously alongside ISDN, making the transition easier.
The transition phase does not interrupt business activities and offers more scope to test the system’s robustness.
2. Auditing the current system
Audit the existing software’s infrastructure and bandwidth before proceeding with the switch. SIP providers use the initial audit to outline the devices they need to install to increase the bandwidth and offer satisfactory services.
As with any audit, run multiple checks to find the gaps in your system. The audit process includes measuring data bandwidth and the requirement for additional connection lines.
3. Installing the new system
SIP installations require much less physical infrastructure than a normal ISDN connection. On-site storage of physical assets and their maintenance also decreases with the installation of SIP. And since it can work alongside ISDN, it doesn’t disrupt your regular business activities.
4. Testing the system
SIP trunking can be integrated with modern communication software, like Skype. The systems also contain built-in continuity features. The SIP providers extensively test the systems before taking them live.
5. Take the program to live
After all the necessary checks are done, it is time to take the entire system live. Depending on your installation plan, this phase can take a long time or be done within hours.
Conclusion
The inevitable switching off of ISDN will force organizations to move to more advanced network systems if they haven’t already. However, instead of waiting for the deadline, it’s crucial to be proactive and seek out reliable and credible VoIP service providers.
You can easily integrate the VoIP system with CRM and Helpdesk software to make it easier for your employees to access customer information while on call. Zero latency transfers your voice in real-time without any input lag. Multiple global servers enable you to get local and international numbers. And advanced features such as AI call rerouting prioritize the calls of high-value customers.
There’s no reason to miss out on all this for a soon-to-be-obsolete technology; it’s finally time to switch to VoIP communications.
FAQs
1. What are ISDN lines?
ISDN lines are a set of communication standards or digital channels used to make calls through the existing telephony infrastructure.
2. What is the difference between ISDN and PSTN?
ISDN can transmit voice, video, and data simultaneously using a single line. In contrast, PSTN or Public Switched Telephone Network only provides a single communication line for voice calls, meaning only one channel can use it at a time.
3. What is the difference between ISDN vs DSL?
Using the internet via ISDN requires a dial-up. DSL requires no such dial-up service. In addition, DSL transmits data faster than ISDN.
4. Why is ISDN being switched off?
Even though ISDN was hailed as revolutionary in the past, it has become stagnant and is on the verge of becoming obsolete with the introduction of advanced technologies like VoIP. As a result, BT found it wiser to switch it off instead of investing more money in its upkeep.
5. What should businesses do to prepare for the switch-off?
Businesses should switch to VoIP or SIP trunking to replace ISDN before switch-off.

Subscribe to our newsletter & never miss our latest news and promotions.









